I was astonished to find that it has been well over four years since I wrote in detail about Bunhill so earlier this week, when the sun was in exactly the right place, I decided to take some pictures and write about it again.
I thought I’d show you the pictures first and then re-publish details of the area’s fascinating history. Around 120,000 people are believed to have been buried here and about 2,500 monuments survive.
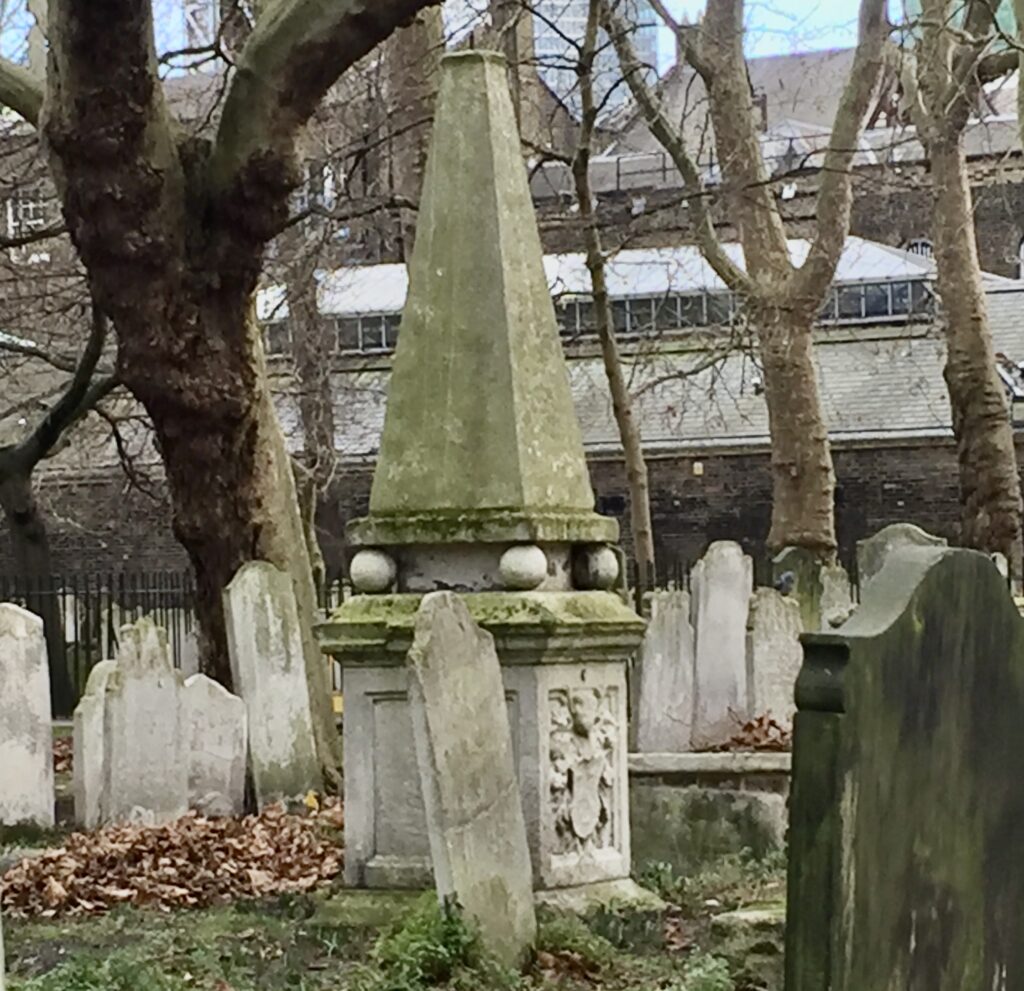
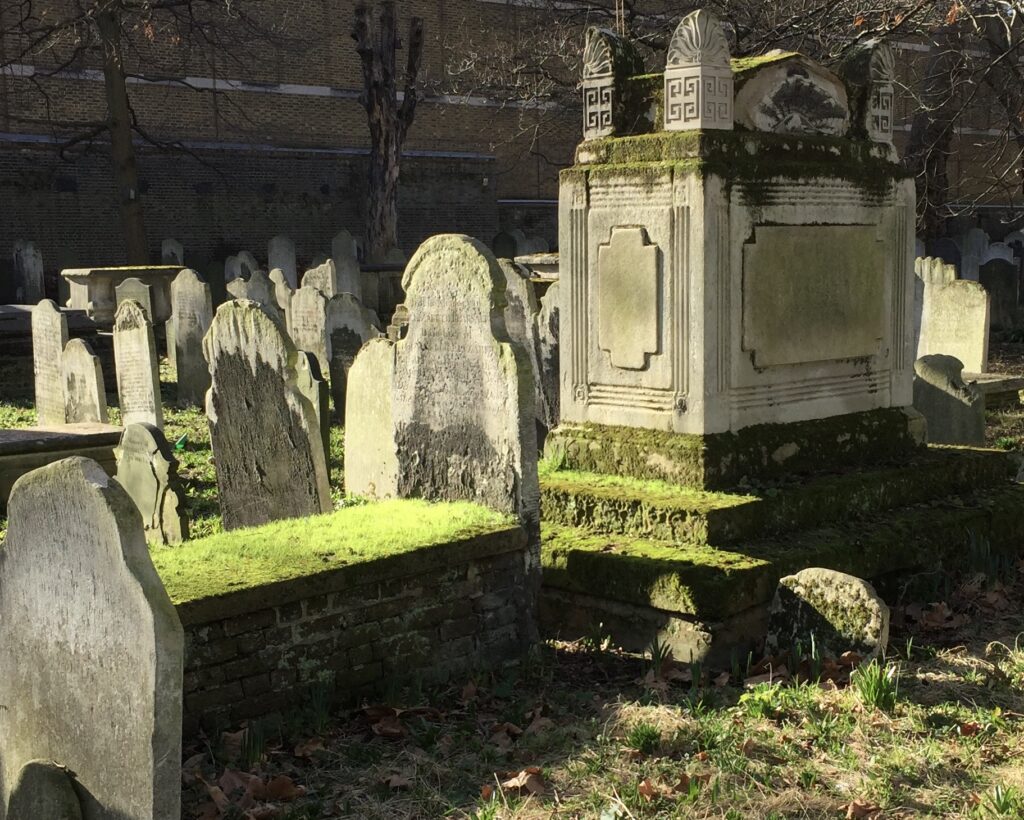









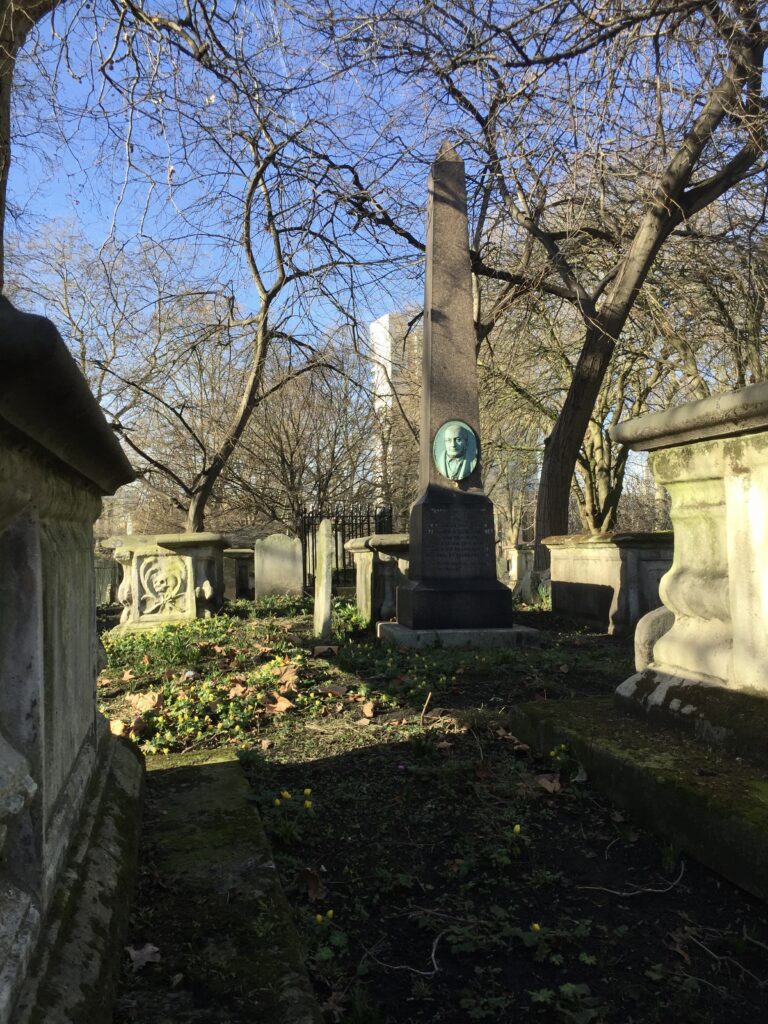
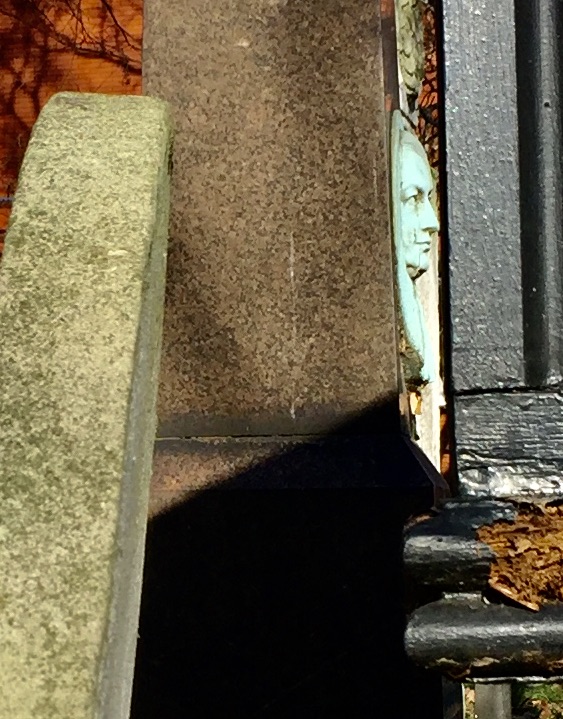
The gentleman whose face is looking out from the obelisk is the Calvinistic Methodist minister, poet and Bible commentator James Hughes …

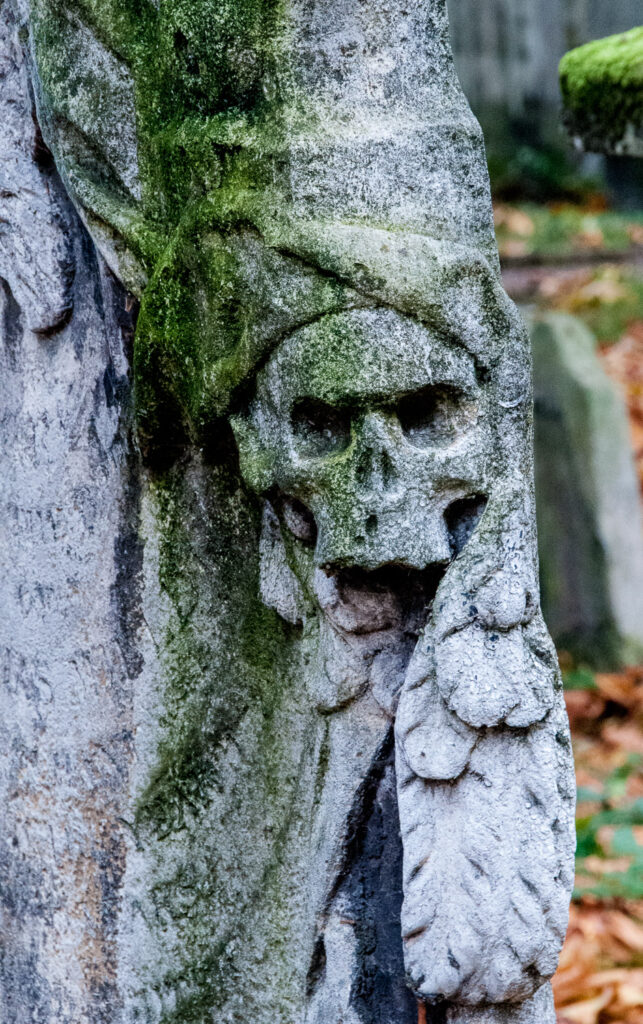
It’s a bit spooky sideways on …

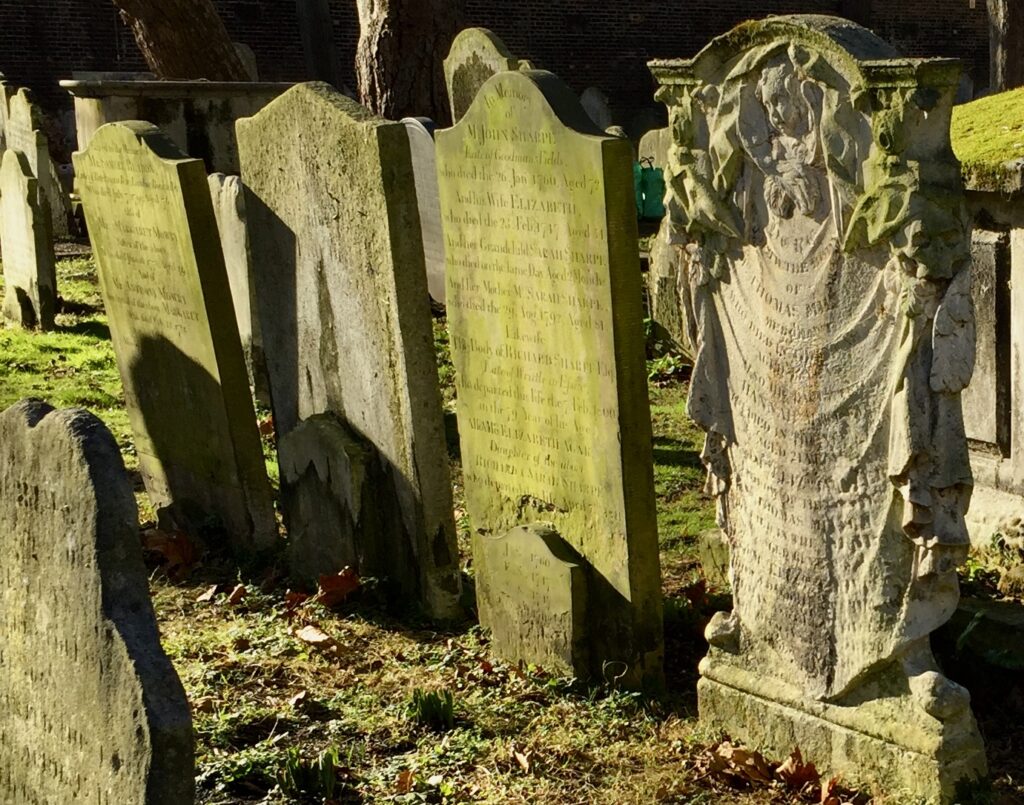
Sadly many of the memorials have deteriorated over the years due to wear and tear and pollution …
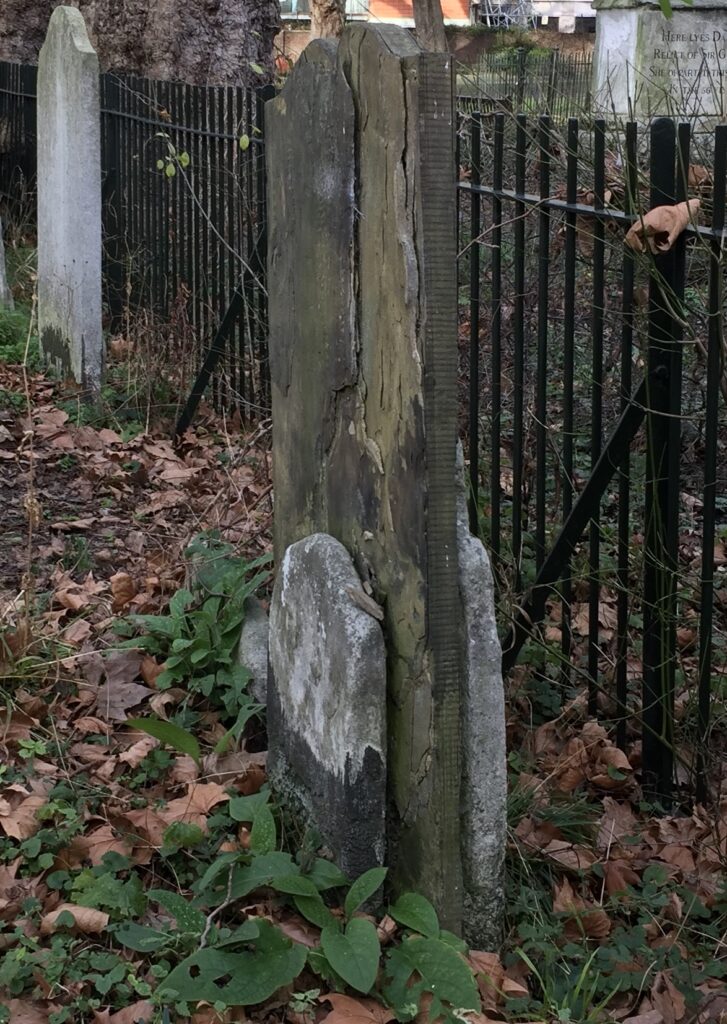

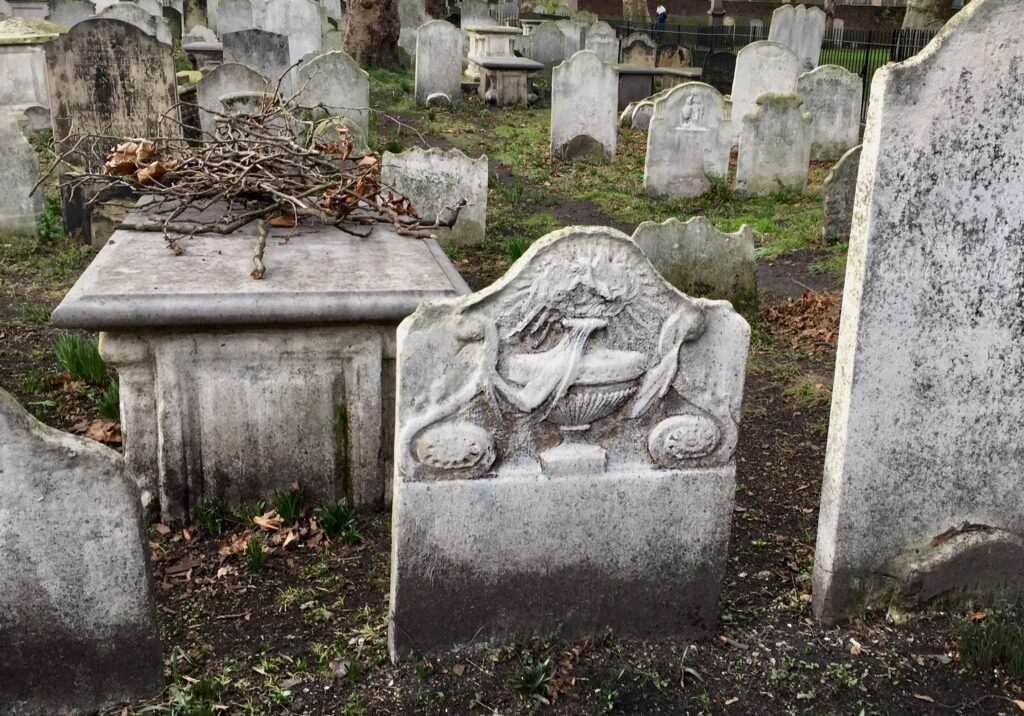
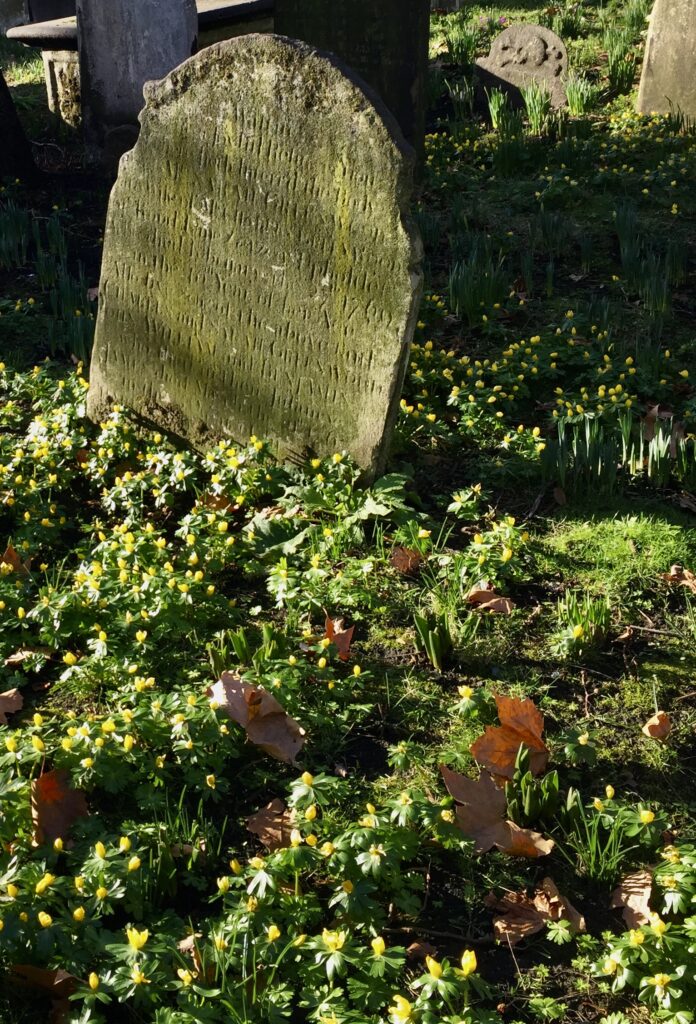
But some inscriptions survive. I was very taken with this marker for the grave of Reverend Joseph Cartwright who died on 5th November 1800 at the age of 72 …

It seems to me that he composed the poem engraved on the stone himself (sadly the last few lines are obliterated). Here it is …
What if death may sleep provide
Should I be of death afraid.
What if beams of opening day
Shine around my breathless clay.
Tender friends a while may mourn
Me from their embraces torn.
Dearer better friends I have
In the realm beneath the grave.
I have written before about some of the more famous memorials but here are a few of them again.
There is the extraordinary tomb of Dame Mary Page …
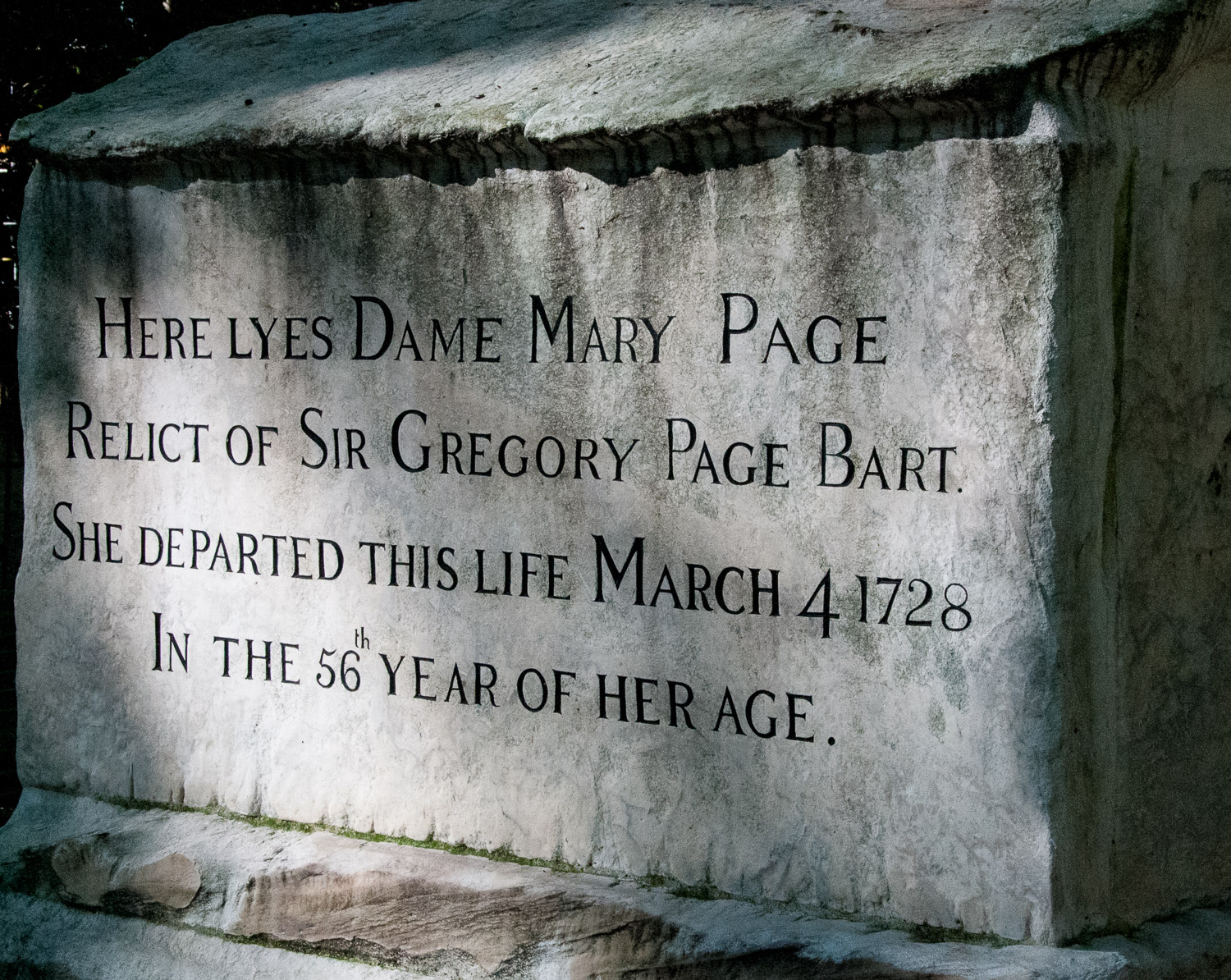
It appears that Mary Page suffered from what is now known as Meigs’ Syndrome and her body had to be ‘tap’d’ to relieve the pressure. She had to undergo this treatment for over five years and was so justifiably proud of her bravery and endurance she left instructions in her will that her tombstone should tell her story. And it does …

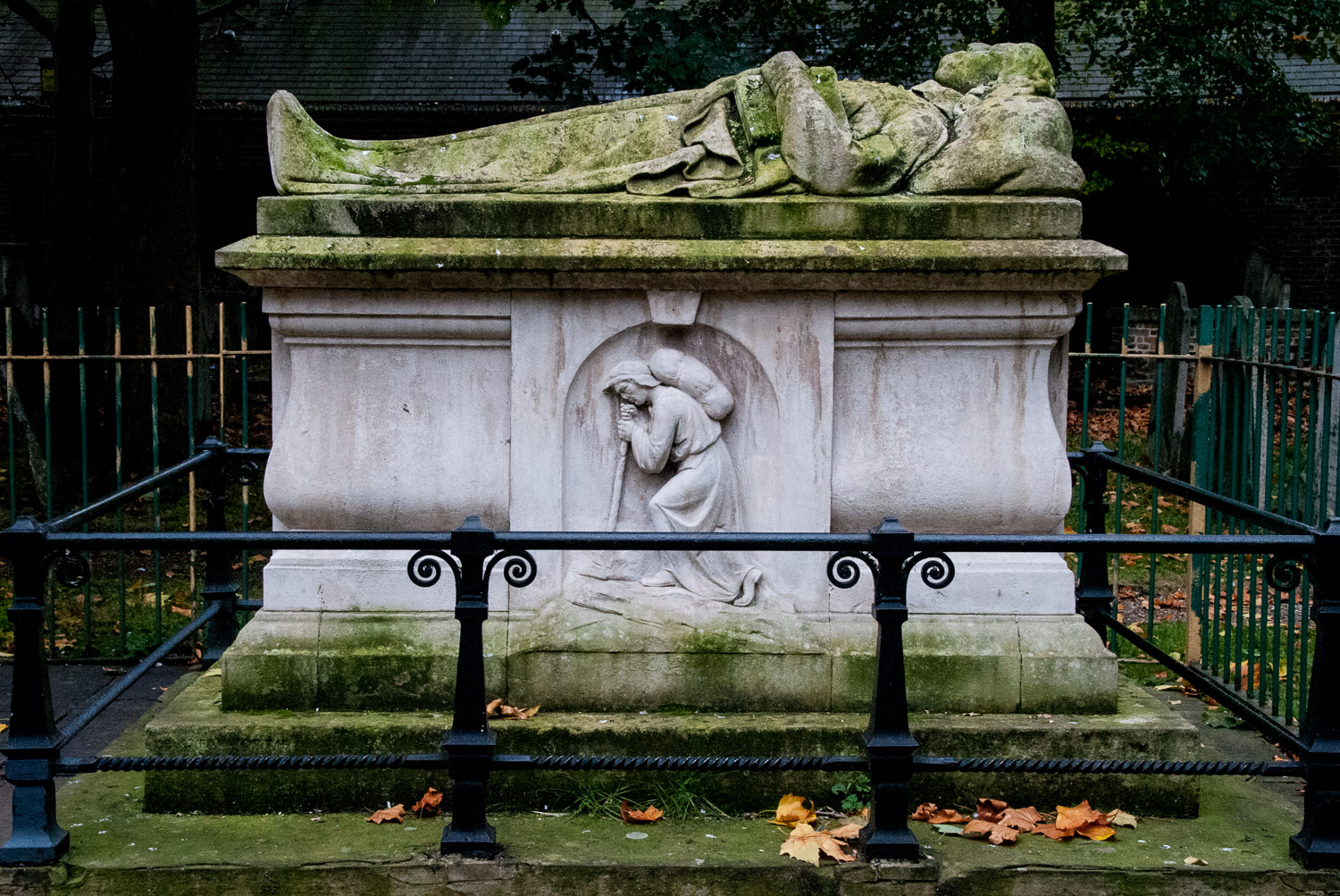
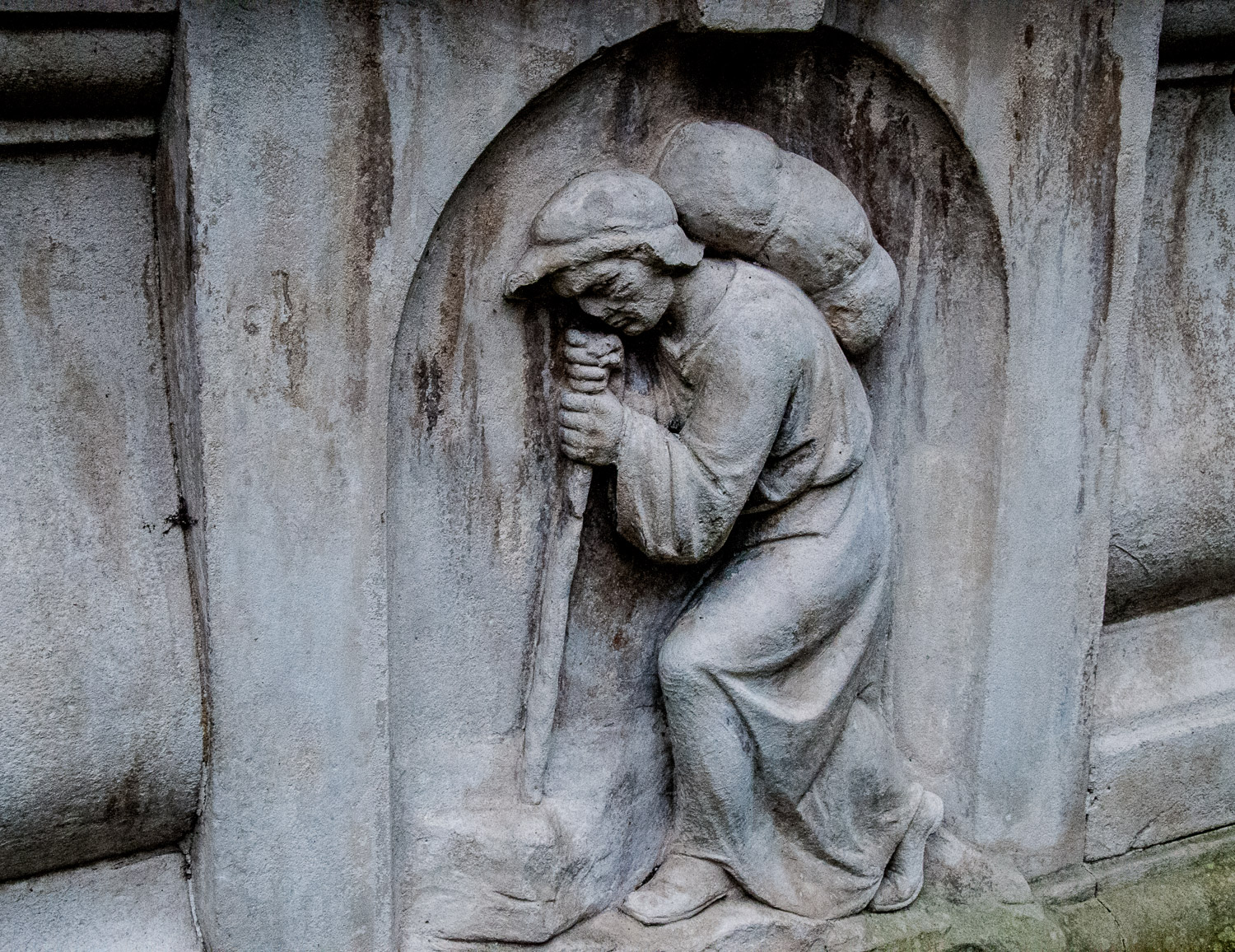
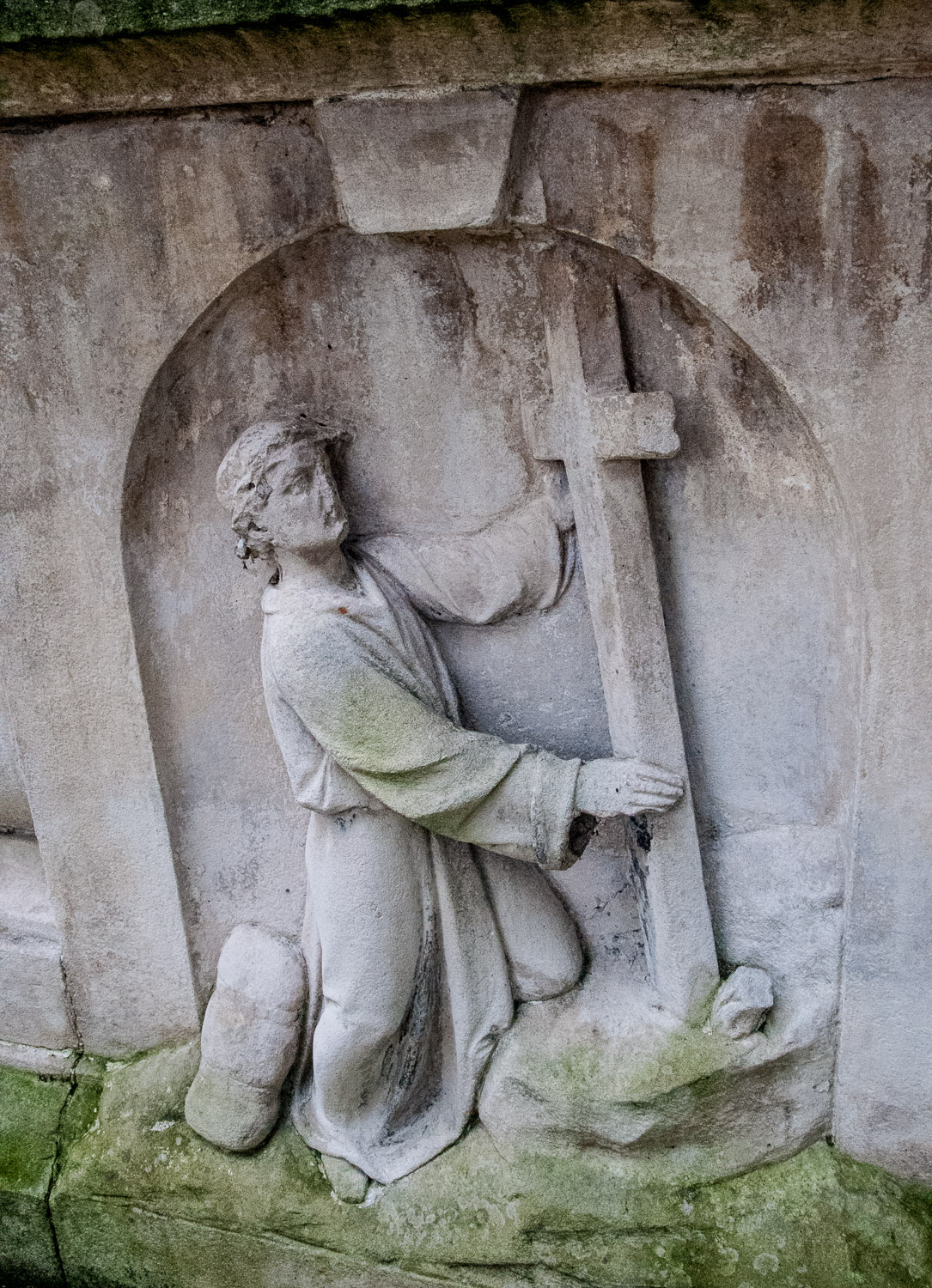
Further on is John Bunyan’s tomb of 1689. It is not quite what it seems since the effigy of the great man and the bas-reliefs (inspired by Pilgrim’s Progress) were only added in 1862 when the tomb was restored. A preacher who spent over a decade in jail for his beliefs, he holds the bible in his left hand. He started the Christian allegory Pilgrim’s Progress whilst imprisoned and it became one of the most published works in the English language.



Bunhill is a nice place for a quiet spot of lunch …

William Blake’s final resting place was once lost but the present day Blake Society finally traced where it was. In August 2018 a beautiful stone was placed there exactly 191 years after his death …

Here’s some Bunhill history for those of you who might be interested.
The history of the land is fascinating. Owned by the Dean & Chapter of St Paul’s Cathedral between 1514 and 1867, it was continuously leased to the City Corporation who themselves sub-leased it to others. The name Bunhill seems to have been a corruption of the word Bonehill. Theories range from people being interred there during Saxon times to the suggestion that various types of refuse, including animal bones from Smithfield, were disposed of there. However, an extraordinary event in 1549 made the name literally true.
Since the 13th century corpses had been buried in St Paul’s churchyard just long enough for the flesh to rot away, after which the bones were placed in a nearby Charnel House ‘to await the resurrection of the dead’. After the Reformation this was seen as an unacceptable Popish practice, the Charnel House was demolished, and 1,000, yes 1,000, cartloads of bones were dumped at Bunhill. A City Golgotha, it is said the the resulting hill was high enough to accommodate three windmills.
In 1665 it was designated a possible ‘plague pit’ but there is no evidence that it was used as such. At the same time, however, a crisis arose concerning St Paul’s, the ‘noisome stench arising from the great number of dead’ buried there. Many other parishes had the same problem and the Mayor and Aldermen were forced to act quickly as a terrible smell of putrefaction was permeating the City. After negotiations with the existing tenants, the ‘new burial place in Bunhill Fields’ was created and had been walled in by the 19th October that year with gates being added in 1666.
The Act of Uniformity of 1663 had established the Church of England as the national church and at the same time established a distinct category of Christian believers who wished to remain outside the national church. These became known as the nonconformists or dissenters and Bunhill became for many of them the burial ground of choice due to its location outside the City boundary and its independence from any Established place of worship.
The last burial took place in January 1854 and the area was designated as a public park with some memorials being removed and some restored or relocated. Heavy bombing during the war resulted in major landscaping work and the northern part was cleared of memorials and laid out much as it is now with grassy areas and benches.
Across City Road you can see the house where the founder of Methodism, John Wesley, once lived. I hope to write about it soon …

If you would like to follow me on Instagram here is the link …
