I think the lockdown is finally getting to me. I usually don’t have much trouble thinking of a theme for the blog but this week I have failed. So instead, I just wandered around a still quiet City with my camera waiting to see what caught my eye. These are the results – I hope you find some of them interesting.
Now the pavements are deserted, it’s easier to look upwards as you walk and see what you might have missed on previous occasions.
The Victorians paid a lot of attention to decorative detail and I really liked these two faces, carved into bricks, looking out over London Wall. I’ve nicknamed them Beauty …
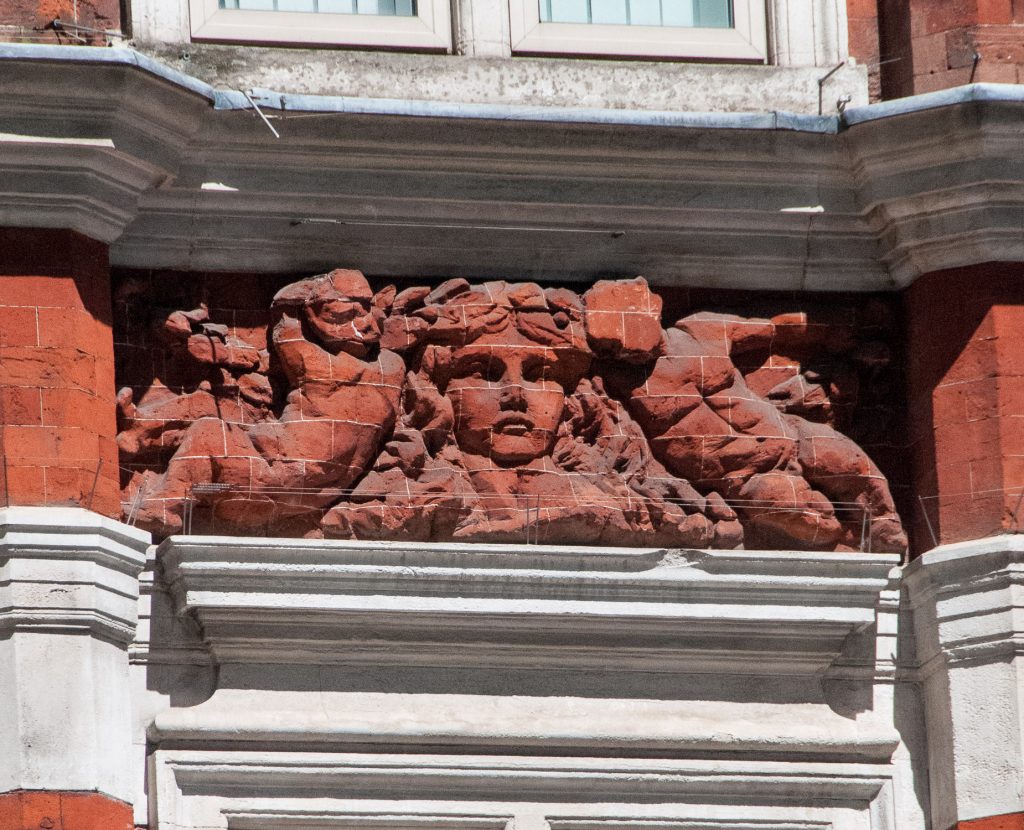

… and the beast …
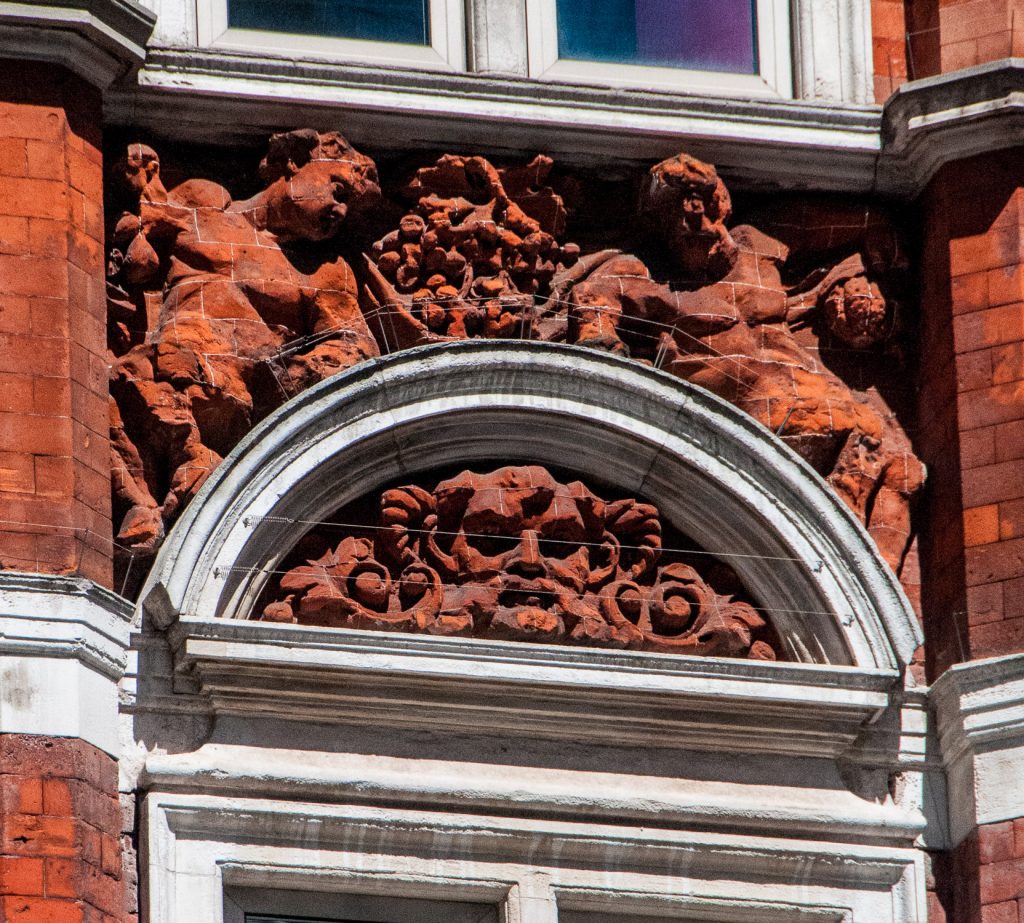

And while on the subject of beauties and beasts, take a look at this view from Gresham Street …
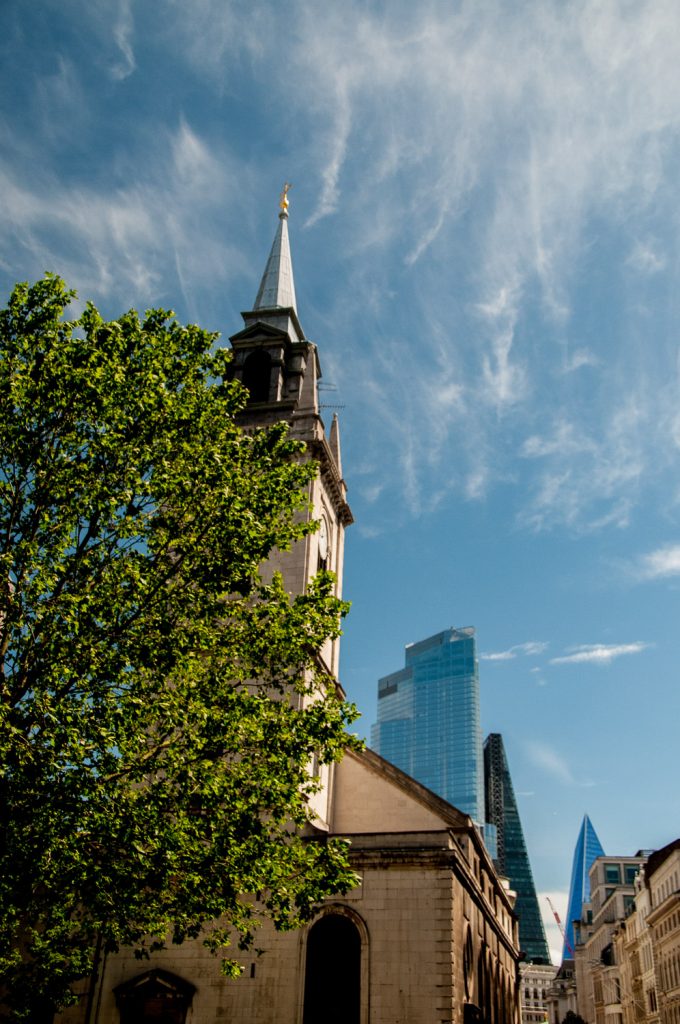

The church is St Lawrence Jewry and behind it some modern buildings that I like, the Cheesegrater and the Scalpel, and one I don’t, a characterless glass monster growing on Bishopsgate.
There’s a nice little pond in front of the church …
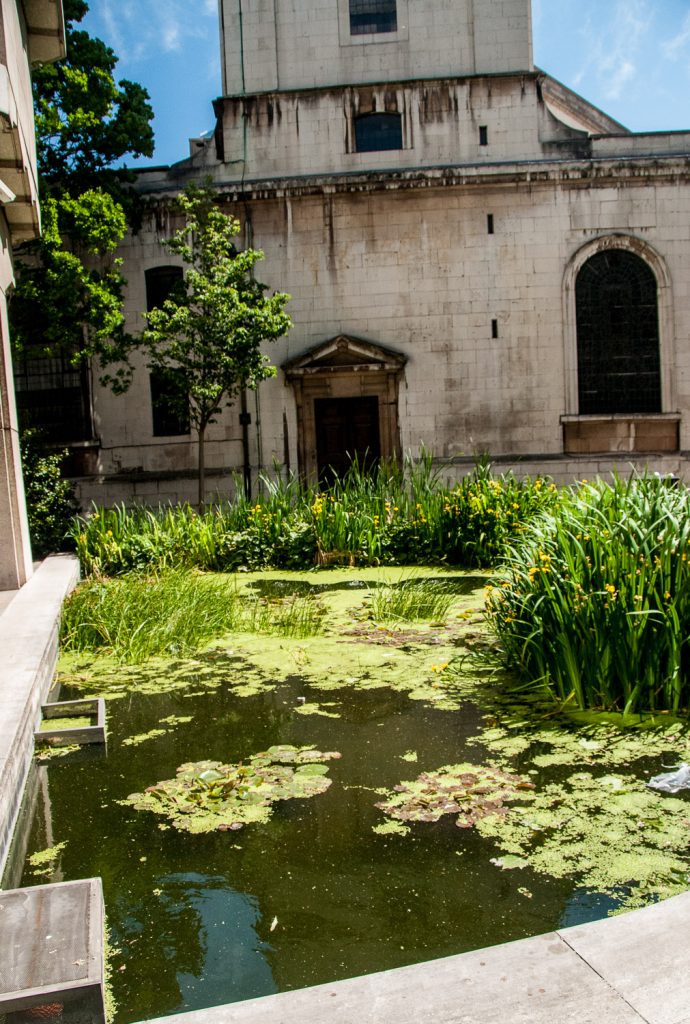

It’s home to these Arum Lilies and Irises …
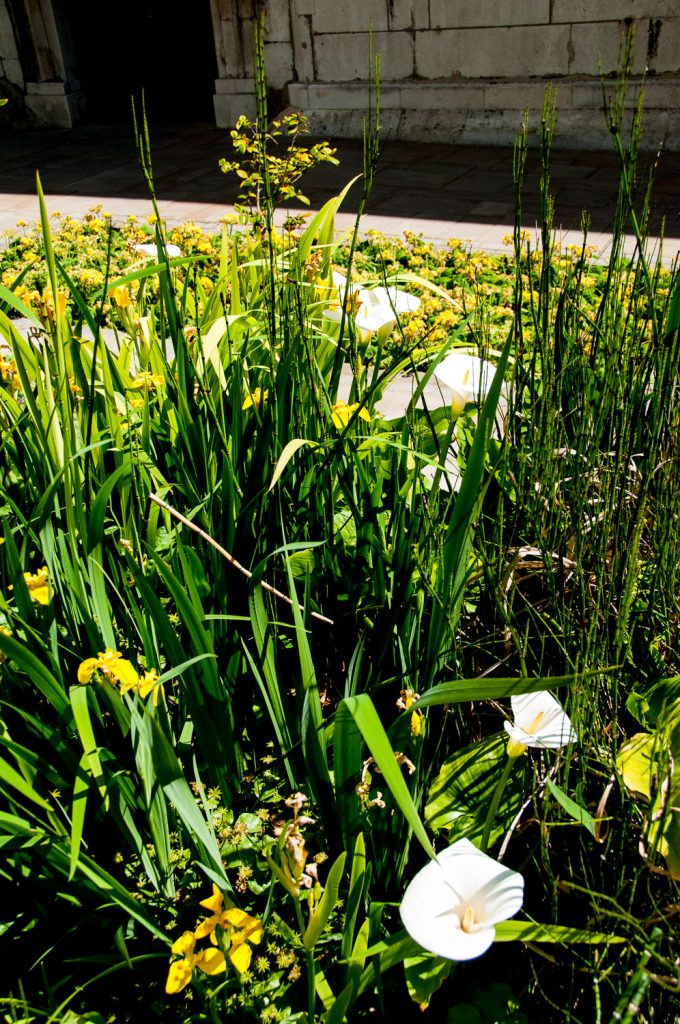

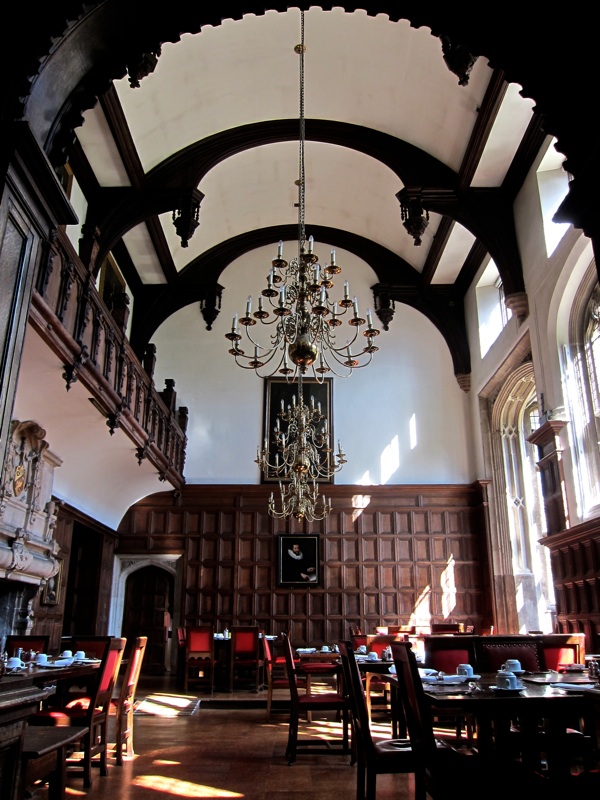
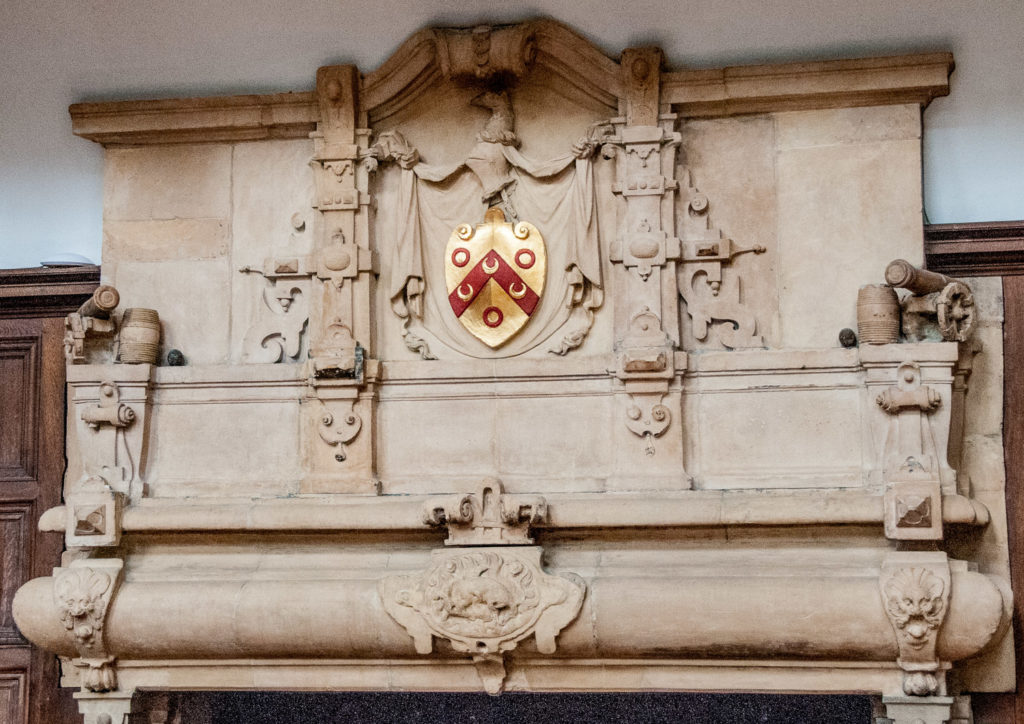
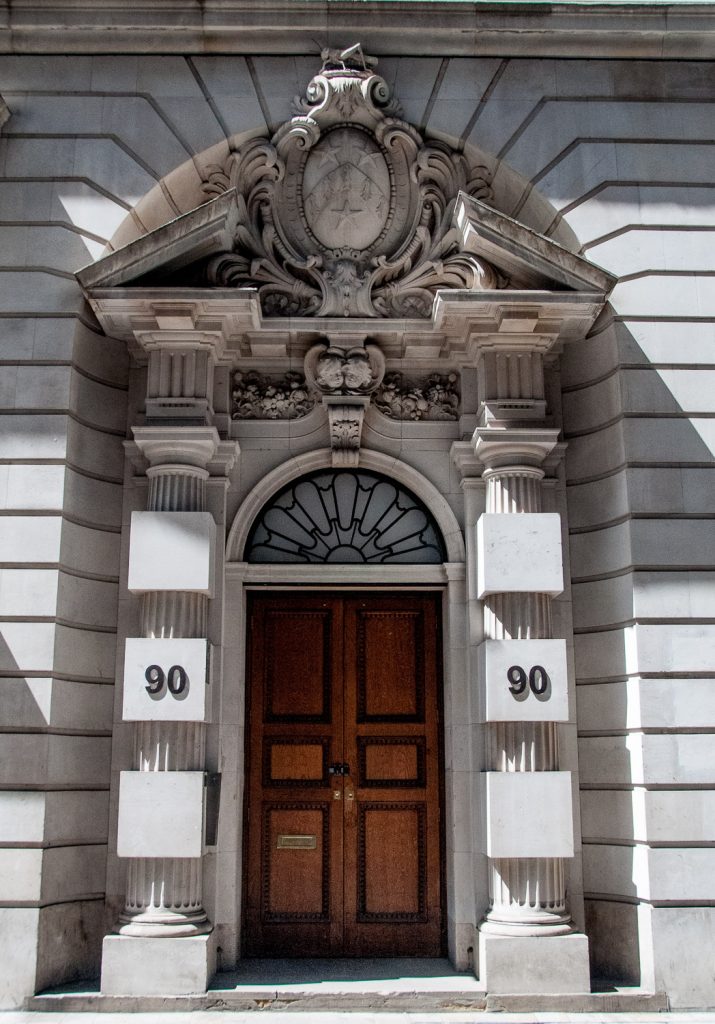
I have written before about Thomas Gresham and the college he founded was once based here at 90 Basinghall Street until 1991 (EC2V 5AY) …

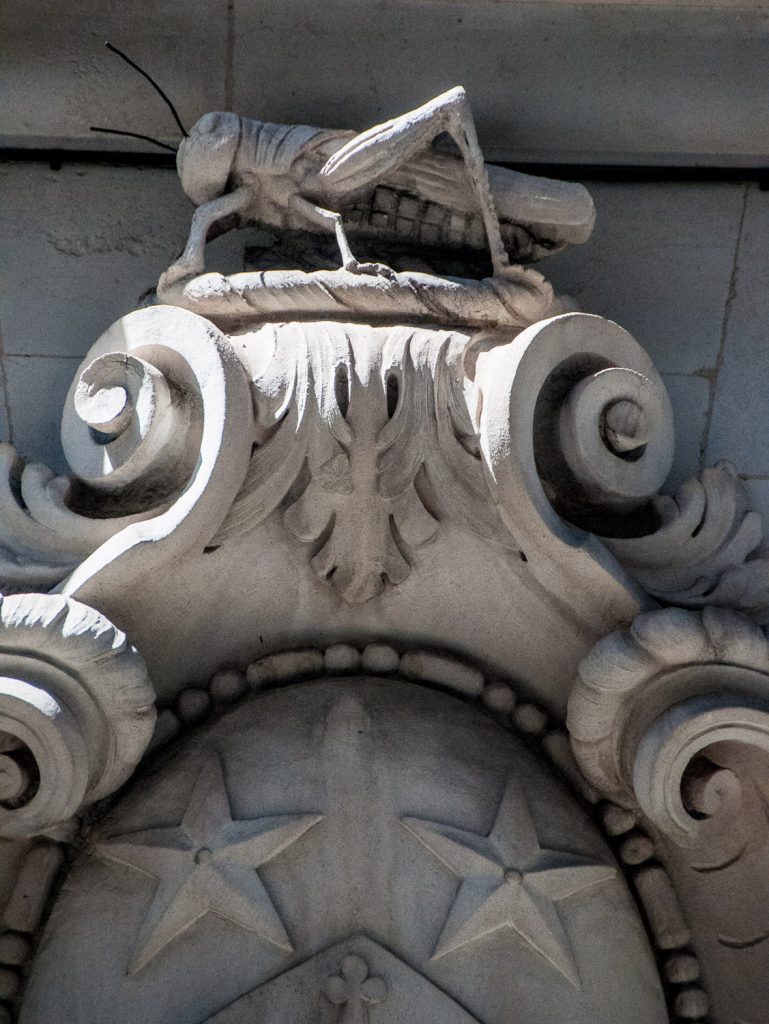
Above the coat of arms rests the symbolic Gresham grasshopper …

The sun was perfectly placed to illuminate Ariel or The Spirit of the Winds by Charles Wheeler. She’s positioned on a cupola above the Bank of England on Tivoli Corner …
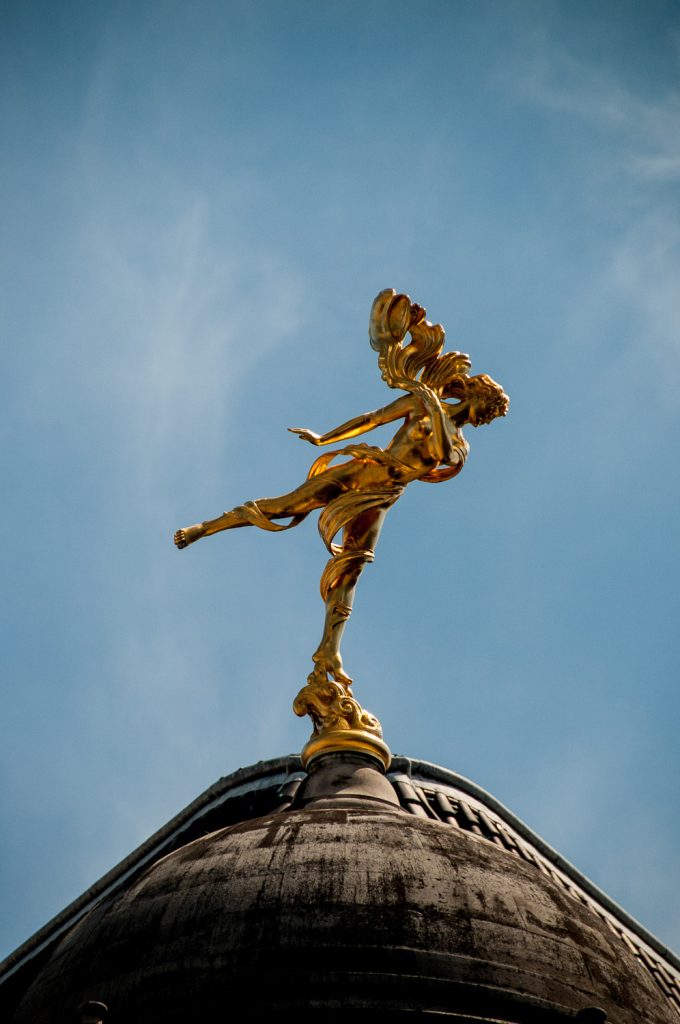

When she was unveiled in 1937 the Bank’s magazine stated …
It is the symbol of the dynamic spirit of the Bank which carries Credit and Trust over the wide world.
Ariel was, of course, the Spirit of the Air in Shakespeare’s Tempest, who by Prospero’s magic could ‘put a girdle around the world in forty minutes’.
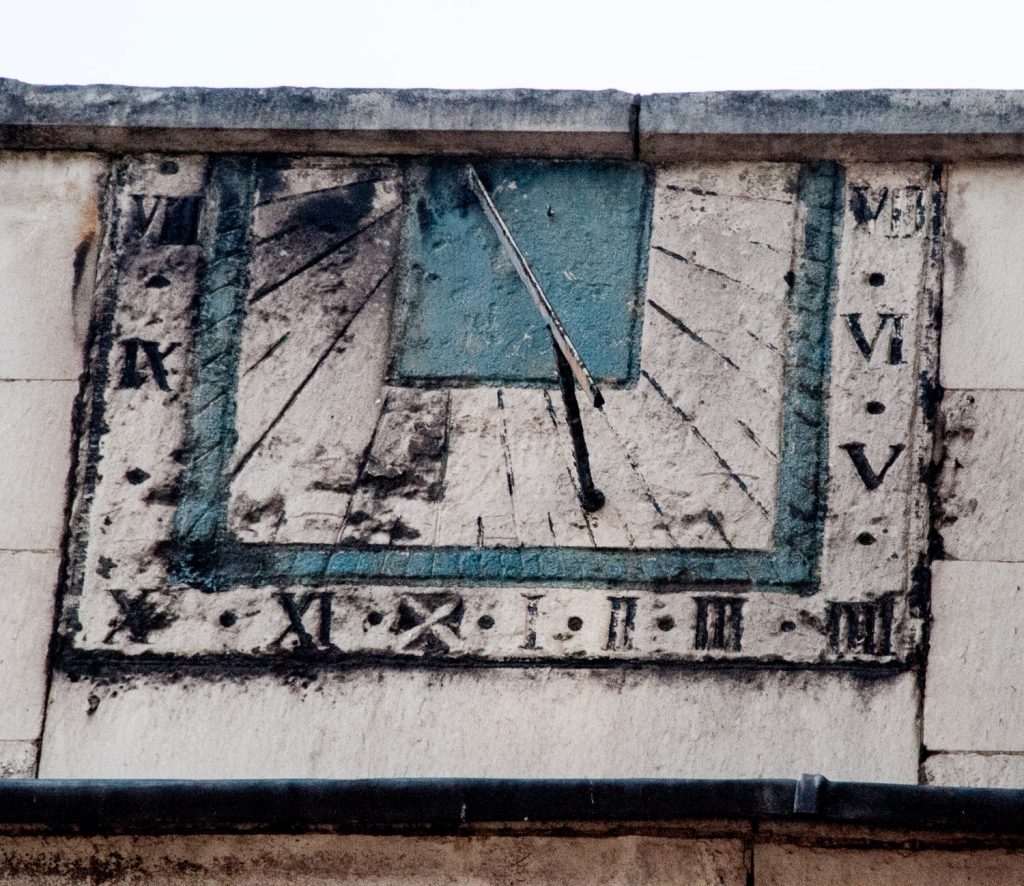
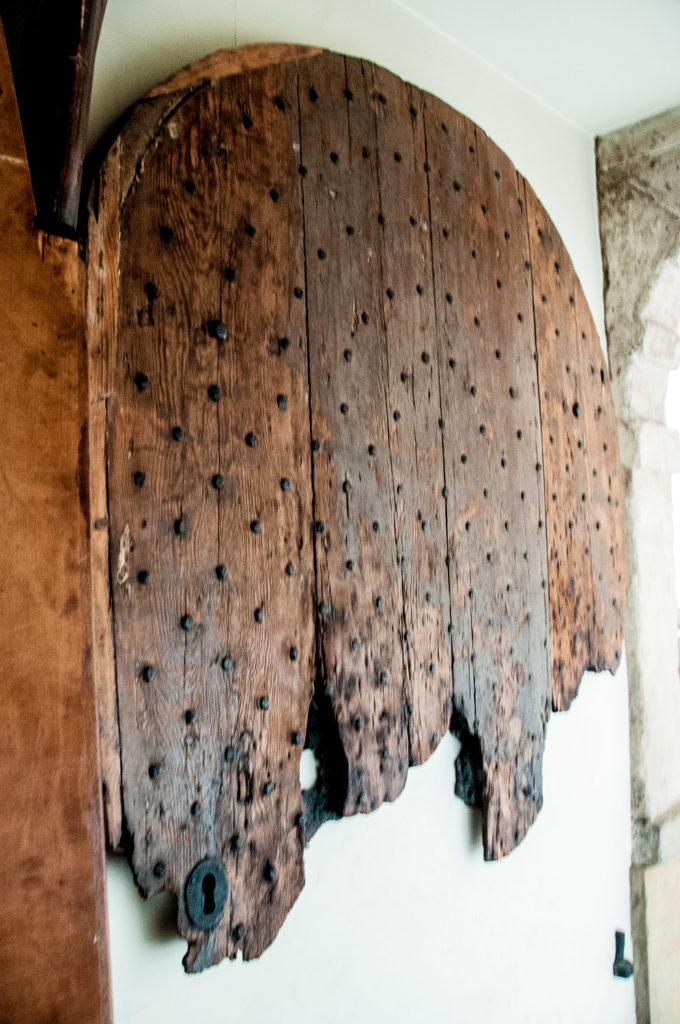
I’m fascinated by this old Wall on London Wall. I can’t find out more about it but it looks Medieval to me (EC2M 5ND) …
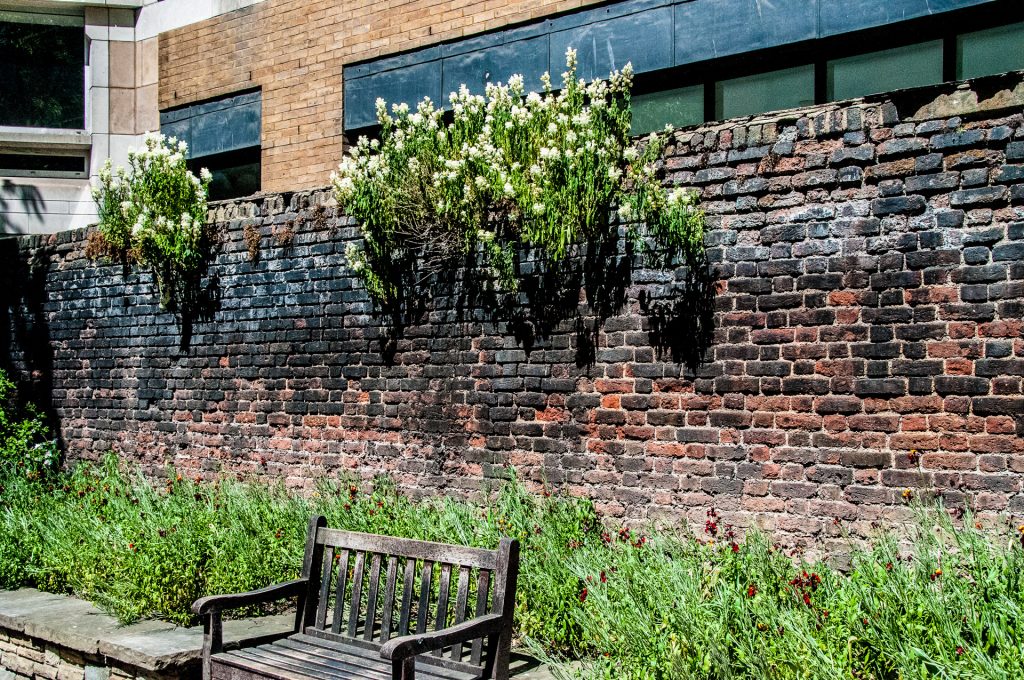

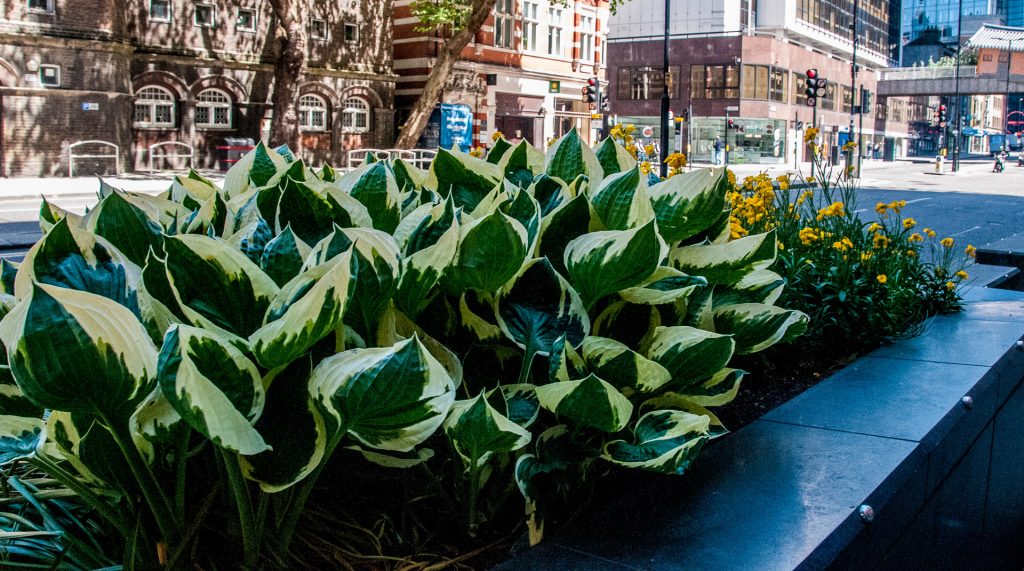
London Wall has lots of examples of the wonderful work the small team of City gardeners do to keep beds and parks looking good all year round …

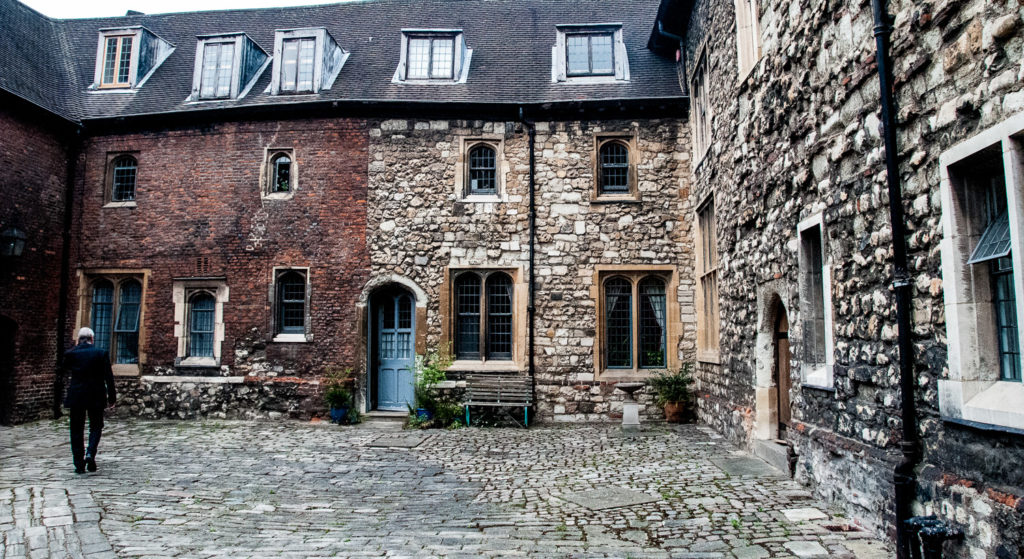
Austin Friars (off Old Broad street) was once the location of an Augustinian Friary until its dissolution in 1538. Walk in through an atmospheric doorway with its charming ghost signs …

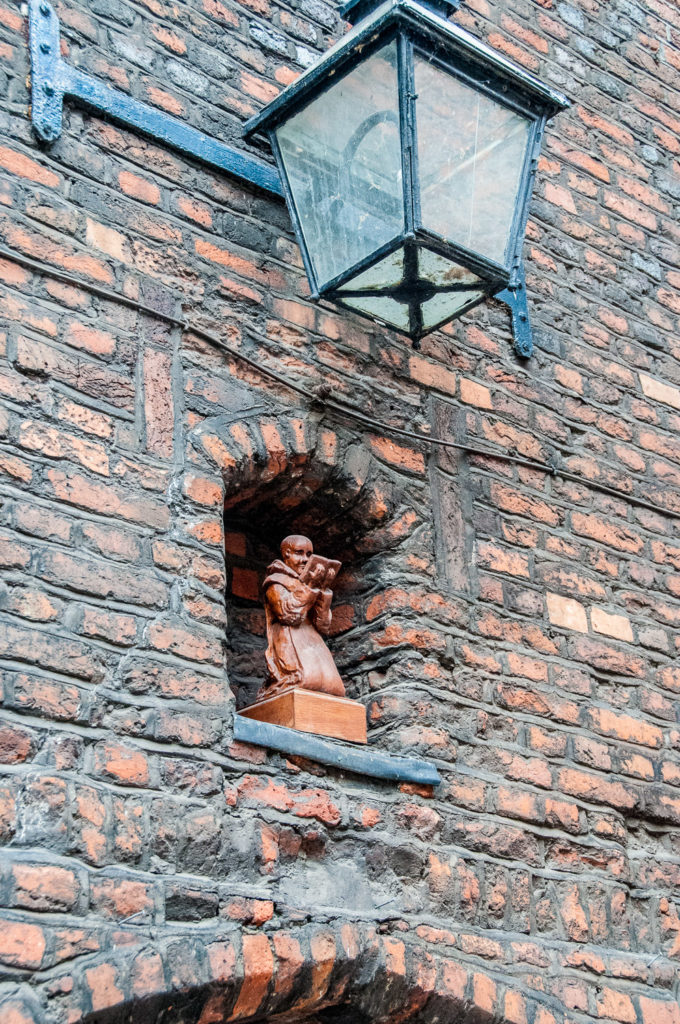
When I visited the sun was in exactly the right place to illuminate the slightly spooky friar who reminds us of the area’s original purpose …
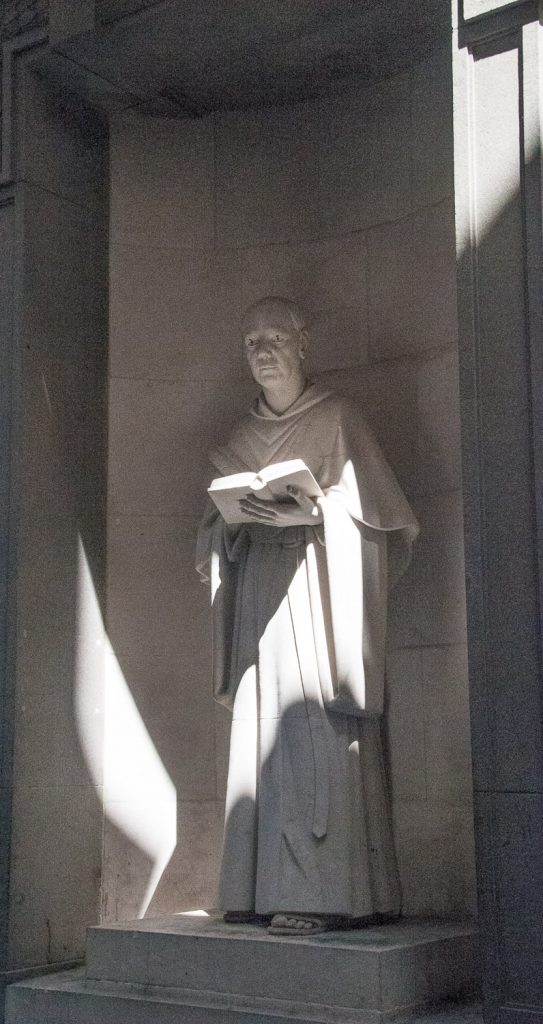

He resides at 4 Austin Friars, was sculpted by T Metcalfe and dates from 1989 (EC2N 2HA).
Near St Giles Cripplegate, the Columbarium is known as ‘one of London’s secret gardens.’ It lies to the east of the church down a flight of stairs. There are some niches on an outside wall and others are in a covered area enclosed by a gate …

And finally, two of the City of London Police’s finest …

… and their riders.
I really enjoyed my little walk and I hope you enjoyed reading about it.
Remember you can follow me on Instagram :