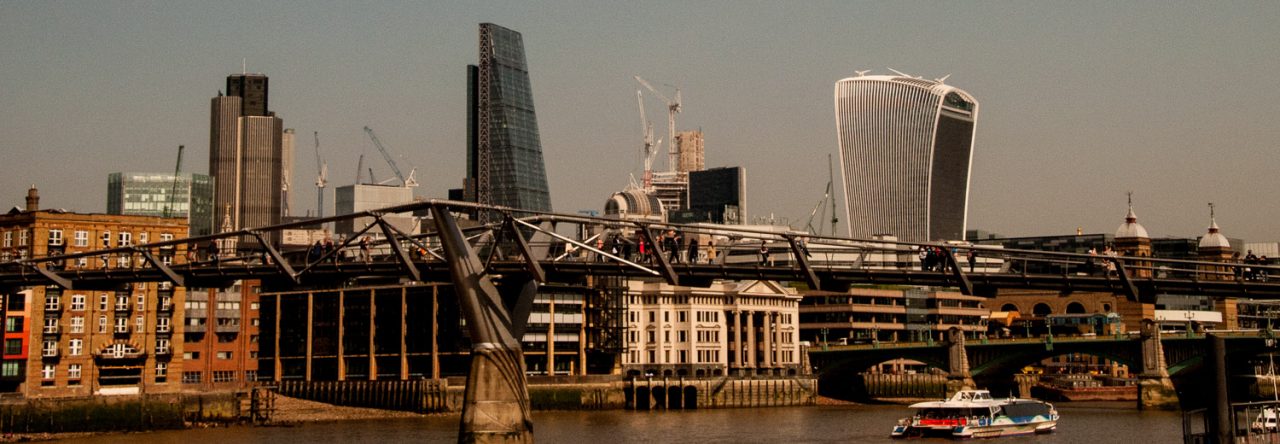
I’m always intrigued by Londoners’ capacity to ignore odd behaviour. For example, I spent a good ten minutes bending over this grating, some of it virtually on my knees, and no one showed the slightest curiosity …

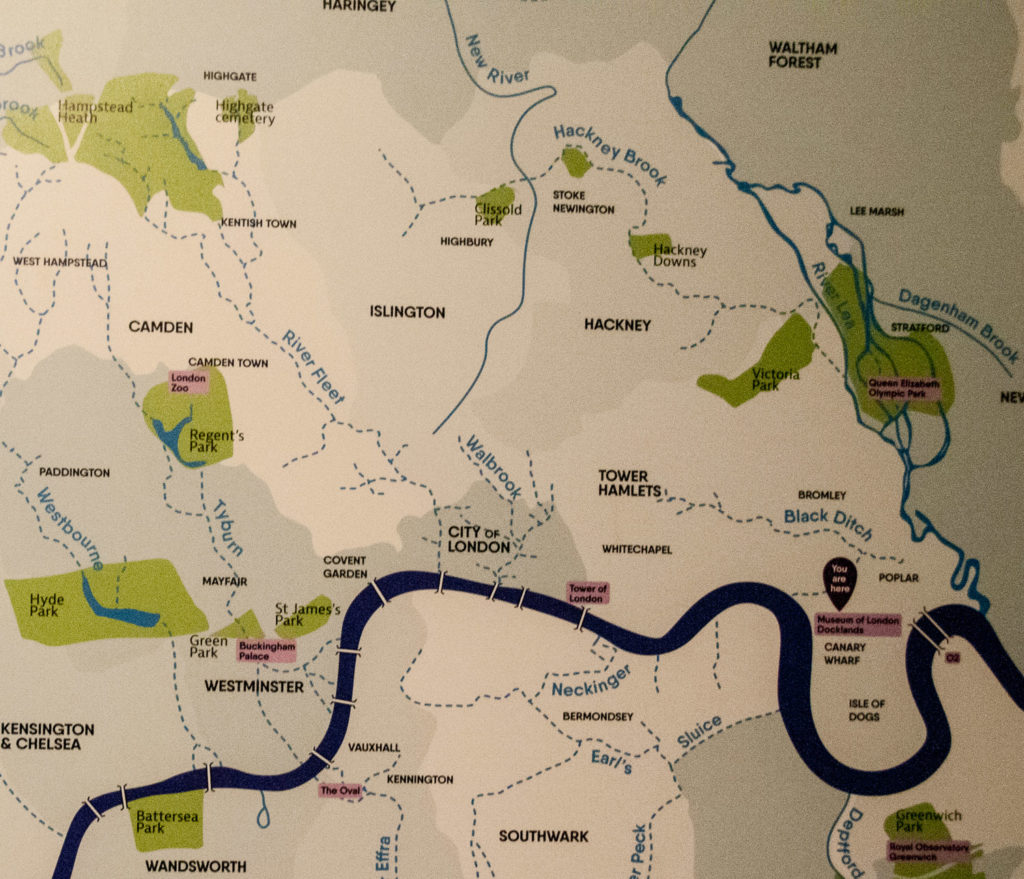
I was, of course, trying to hear the sound of running water since, directly underneath, runs probably the most famous of London’s ‘lost’ subterranean rivers, the Fleet. Its headwaters are two streams on Hampstead Heath, each of which was dammed into a series of ponds in the 18th century. At the southern edge of the Heath these descend underground as sewers which join in Camden Town. The waters flow four miles from the ponds to the River Thames, just underneath Blackfriars Bridge. Incidentally, it didn’t run down Fleet Street, it merely ran past its eastern, lower end.
This map, showing the route of the Fleet and various other waterways, is on display at the excellent Secret Rivers exhibition at the Museum of London Docklands …
Because of its later reputation, I always had a view that the Fleet where it joined the Thames would be a deeply unpleasant place, so this picture rather surprised me …
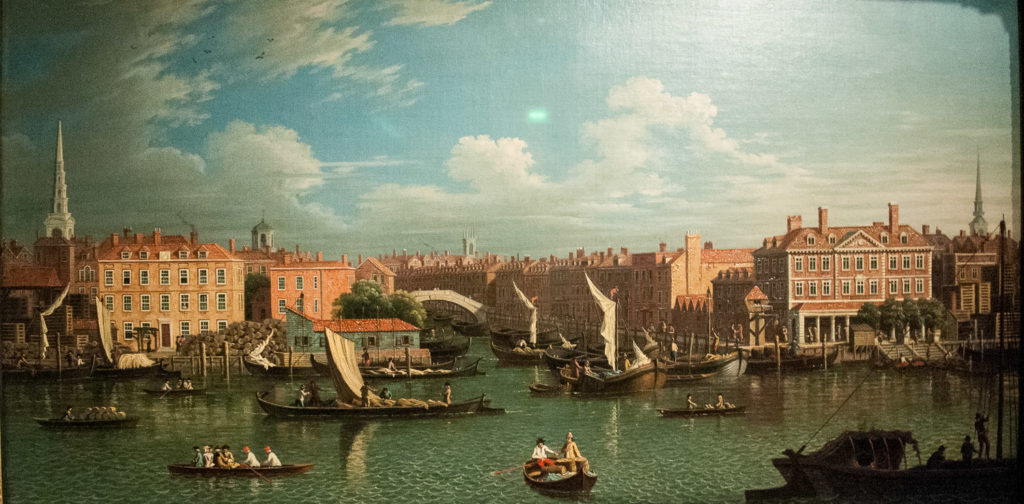
This painting (by a follower of Samuel Scott) was obviously influenced by Canaletto, who was based in England until 1755. Looking north across the Thames, it shows the entrance to the Fleet circa 1750 with Bridewell Foot Bridge, the City Wharf and Dock, and Blackfriars Stairs. The Fleet was developed into a canal up to Holborn, lending this view a Venetian appearance. This grand aspect, however, did not last long as the wharves proved unprofitable and Londoners continued to dump their rubbish in the river.
Originally a green river valley, the Fleet River had been gradually transformed into the Fleet Ditch, infamous for being a source of filth, corruption and disease. Observing a flood during a storm in 1710 Jonathan Swift penned the following lines …
Sweepings from Butchers Stalls, Dung, Guts and Blood,
Drown’d Puppies, stinking Sprats, all drench’d in Mud,
Dead Cats and Turnip-Tops come tumbling down the Flood.
Pope made this small literary contribution in 1728 …
To where Fleet Ditch, with disemboguing streams, rolls the large tribute of dead dogs to the Thames.
On display at the exhibition is sad little exhibit. Found during excavations of the old river bed, it’s a dog’s collar with the inscription ‘Tom at Ye Greyhound Bucklersbury’. Poor Tom.
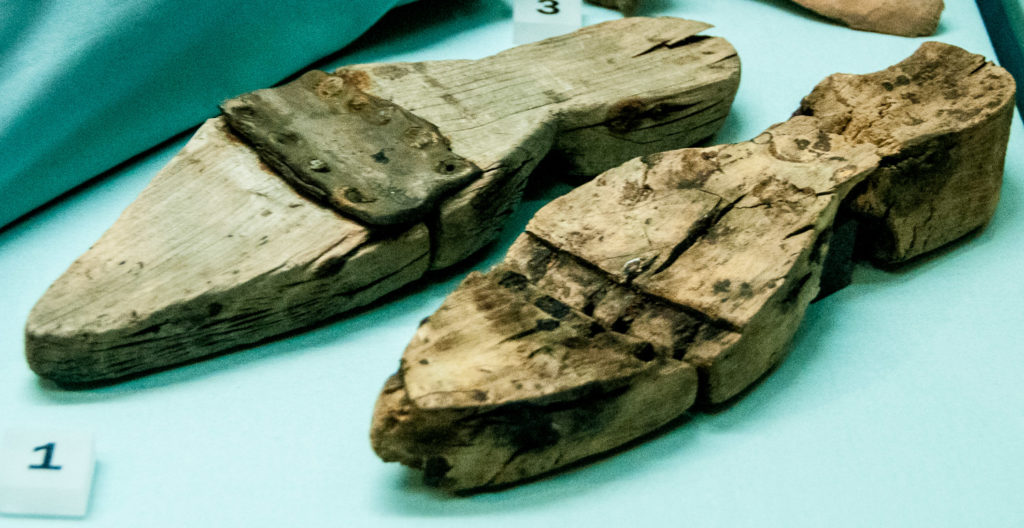
There is a reminder in the exhibition of how muddy and dirty the City’s streets were. This pair of wooden pattens date from the 15th century and were used to protect shoes and raise the wearer above the mud. They have a leather hinge to aid walking …

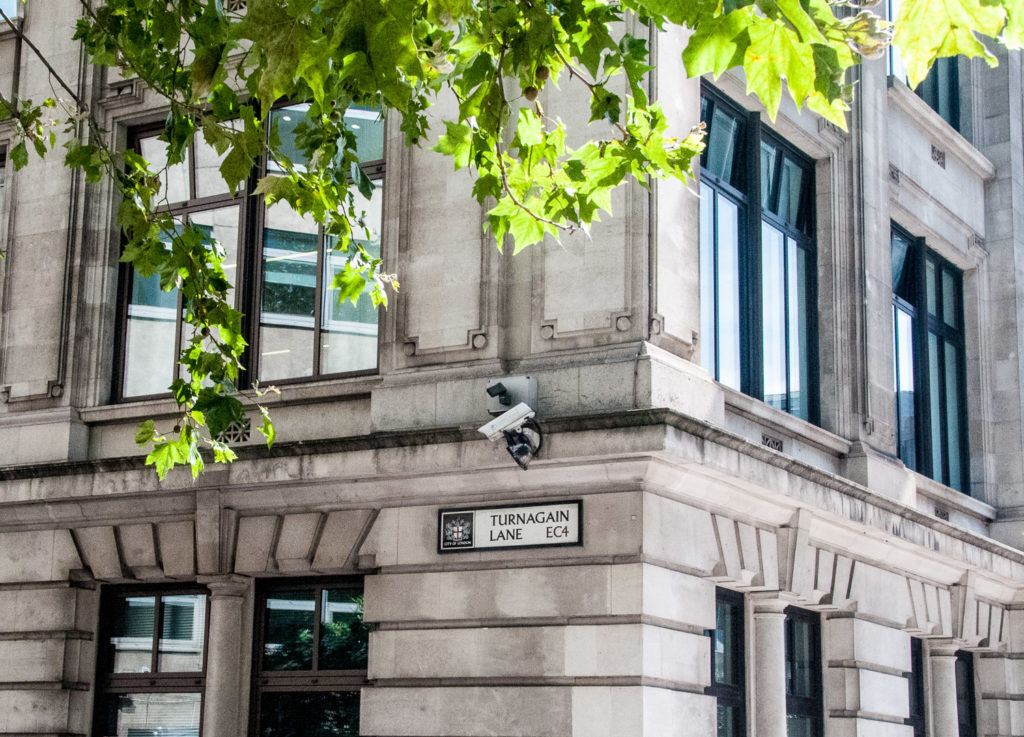
London’s population grew rapidly through the seventeenth century from about 200,000 to about half a million which resulted in a significant rise in the need for coal. This was brought from the north east of the country in barges which offloaded at wharves in the tidal Fleet. Street names that survive today remind us of this …


And the thoroughfare that ended at the canal, so you couldn’t go any further …

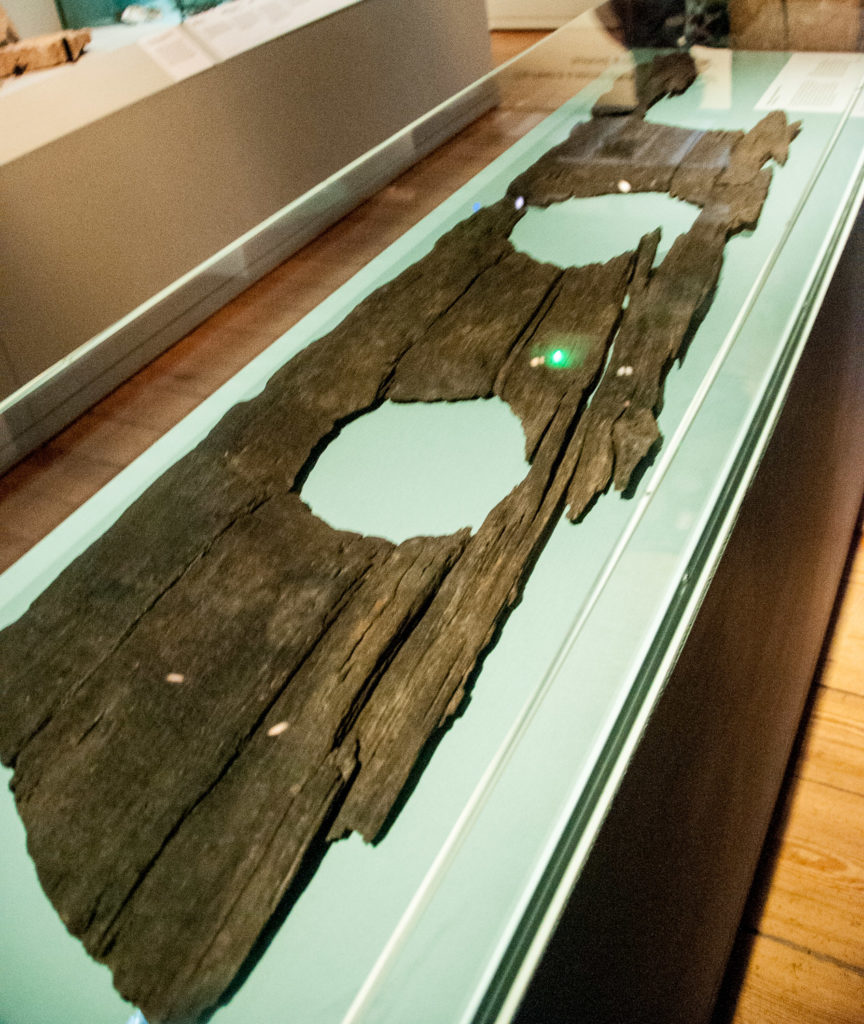
The Fleet Valley from Clerkenwell to the Thames housed many of London’s prisons and all manner of vice was practised in the dingy, stinking claustrophobic rookeries (slums). Nor was there much privacy if you had to go to the loo. This medieval oak three-seater toilet seat was found over cesspit in a yard behind buildings that faced on to modern day Ludgate Hill …

This picture tells a story. It’s an 1841 drawing by Antony Crosby of the Fleet River at Holborn Bridge – note the wooden latrine projecting over the ditch on the left …

Holborn Viaduct was built between 1863 and 1869 in order to span the Fleet and provide level access from east to west – a great improvement in an era of horse-drawn traffic. You can see it reaches over a deep valley …

When I climbed the stairs to take a picture from above a curious City dragon popped his head up to see what I was doing …
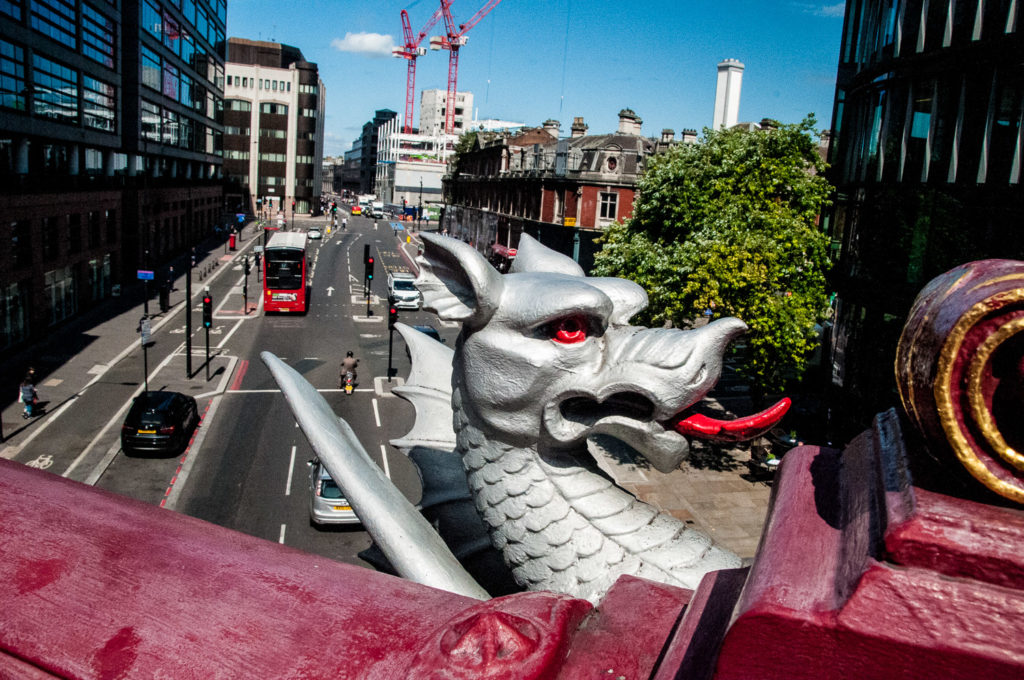

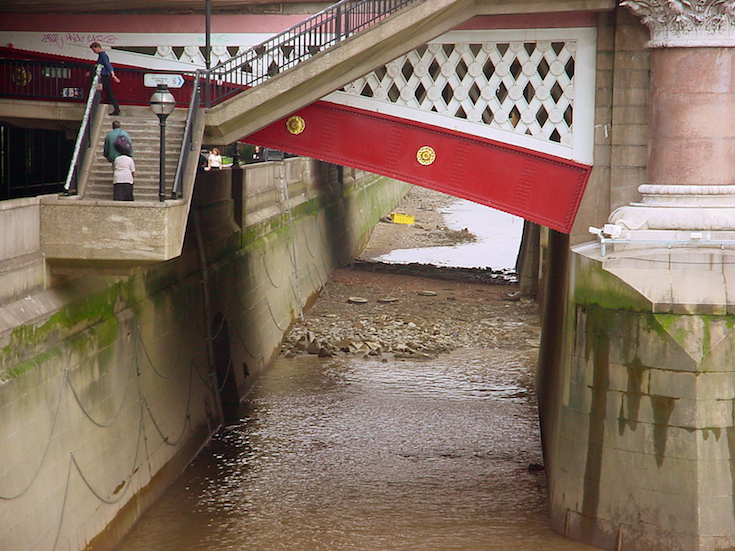
Gradually the entire river was enclosed in Victorian sewer tunnels and it now flows into the Thames under Blackfriars Bridge (just below where the banker Roberto Calvi was found hanged in 1982) …

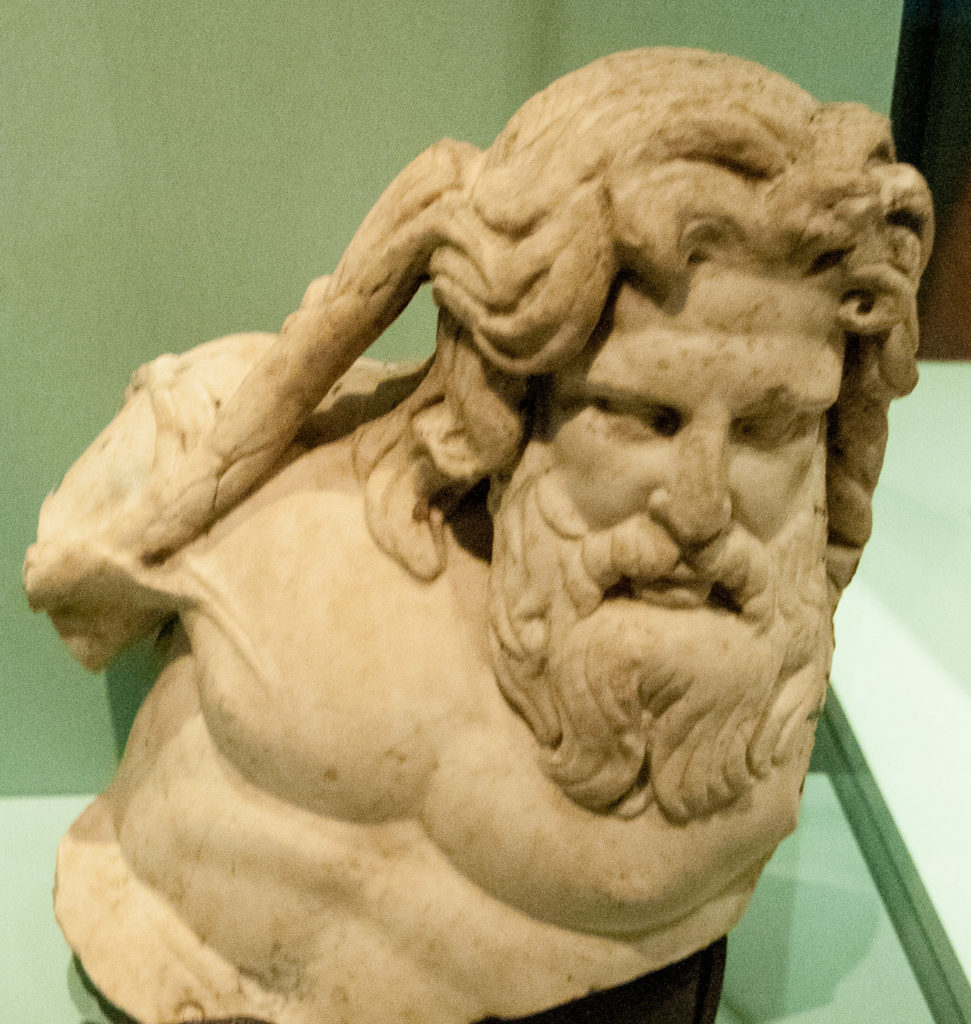
Rivers, such as the Thames and the Walbrook, influenced where the Romans founded Londinium and the Museum of London exhibition also illustrates the fact that our connection to water goes beyond the practical, reaching into the spiritual. While most objects found in London’s rivers are lost items, rubbish or remnants of river-related activities, some cannot be explained so easily. These bear witness to the spiritual importance of rivers.
On display, for example, is this first or second century AD small representation of a river god, possible Neptune, apparently cast or placed into the Walbrook …

And this piece of a marble offering is particularly fascinating …

The inscription has been translated thus:
To the Divinities of the Emperors (and) to the god Mars Camulus. Tiberinius Celerianus, a citizen of the Bellovaci, moritix, of Londoners the first …
It is the first example from the capital to use the word Londiniensi or ‘Londoners’. The language suggests a man who hailed from northern France and probably traded or travelled regularly within that region but whose home seems to have become London.
If you want to read more about Roman London I have written three earlier blogs on the subject: The Romans in London – Mithras, Walbrook and the Games, The Romans in London … and two Roman ladies and The Roman Wall revisited.
The Museum of London Docklands exhibition runs until 27th October this year. I highly recommend it.
