Visiting the Guildhall Art Gallery is always a treat. Exhibitions change all the time and, tucked away near the cloakroom, is the small City of London Heritage Gallery, which is free to enter.
There are not many exhibits but they are usually all fascinating.
Seek out this little display. It contains the William Charter of 1067, the City of London’s oldest document, which tells us what happened when William I reached London after the Battle of Hastings …
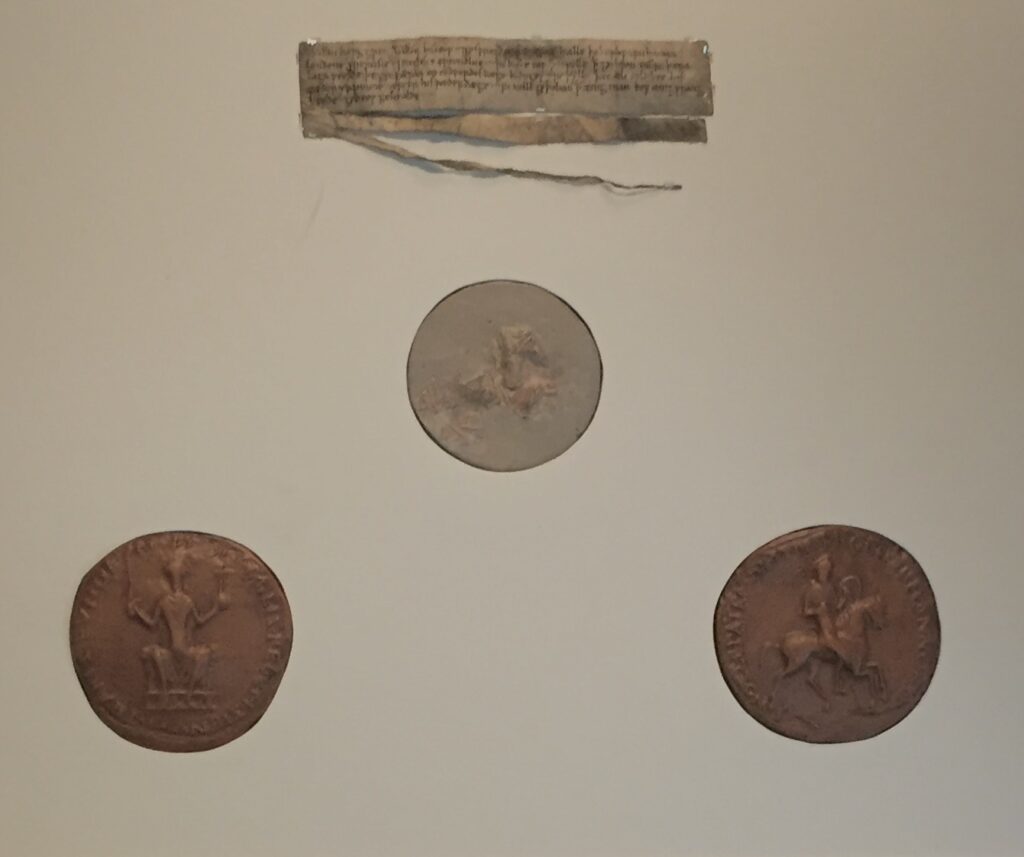

Written on vellum (parchment) in Old English, it measures just six inches by one-and-a-half inches. It also comes complete with one of the earliest surviving seals from William the Conqueror’s reign …

Translated into modern English, the Charter reads as follows:
‘William the king, friendly salutes William the bishop and Godfrey the portreeve and all the burgesses within London both French and English. And I declare that I grant you to be all law-worthy, as you were in the days of King Edward; And I grant that every child shall be his father’s heir, after his father’s days; And I will not suffer any person to do you wrong; God keep you.’
City of London historians point out that one of the citizens’ primary concerns, as expressed by the words – “And I grant that every child shall be his father’s heir, after his father’s days” – was to ensure that their property handed down to the son and heir, rather than attracting the interest of the Crown.
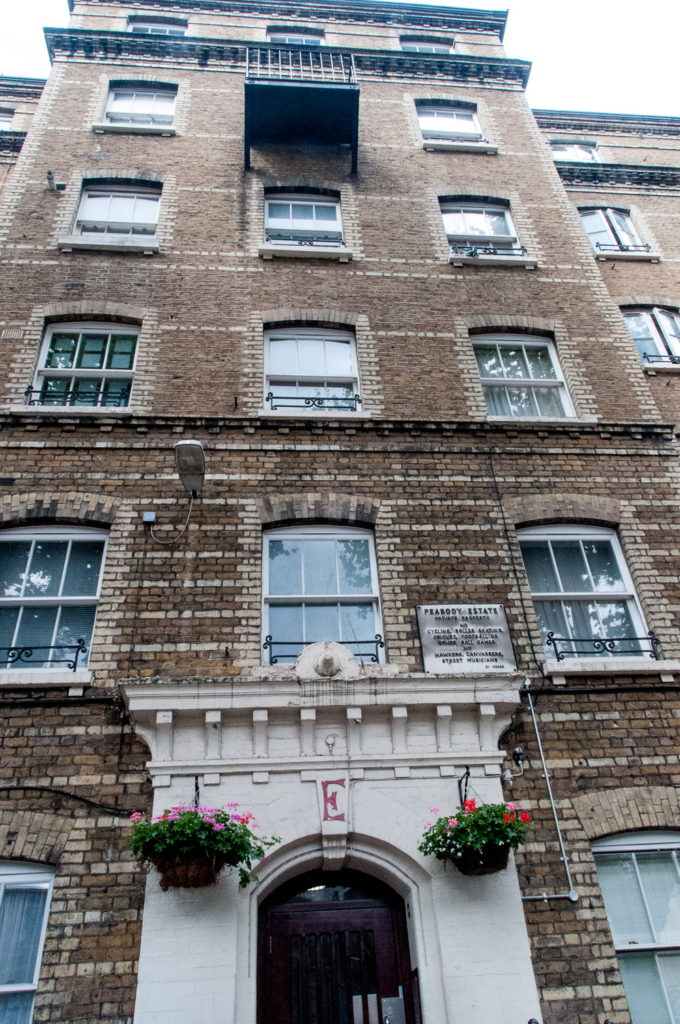
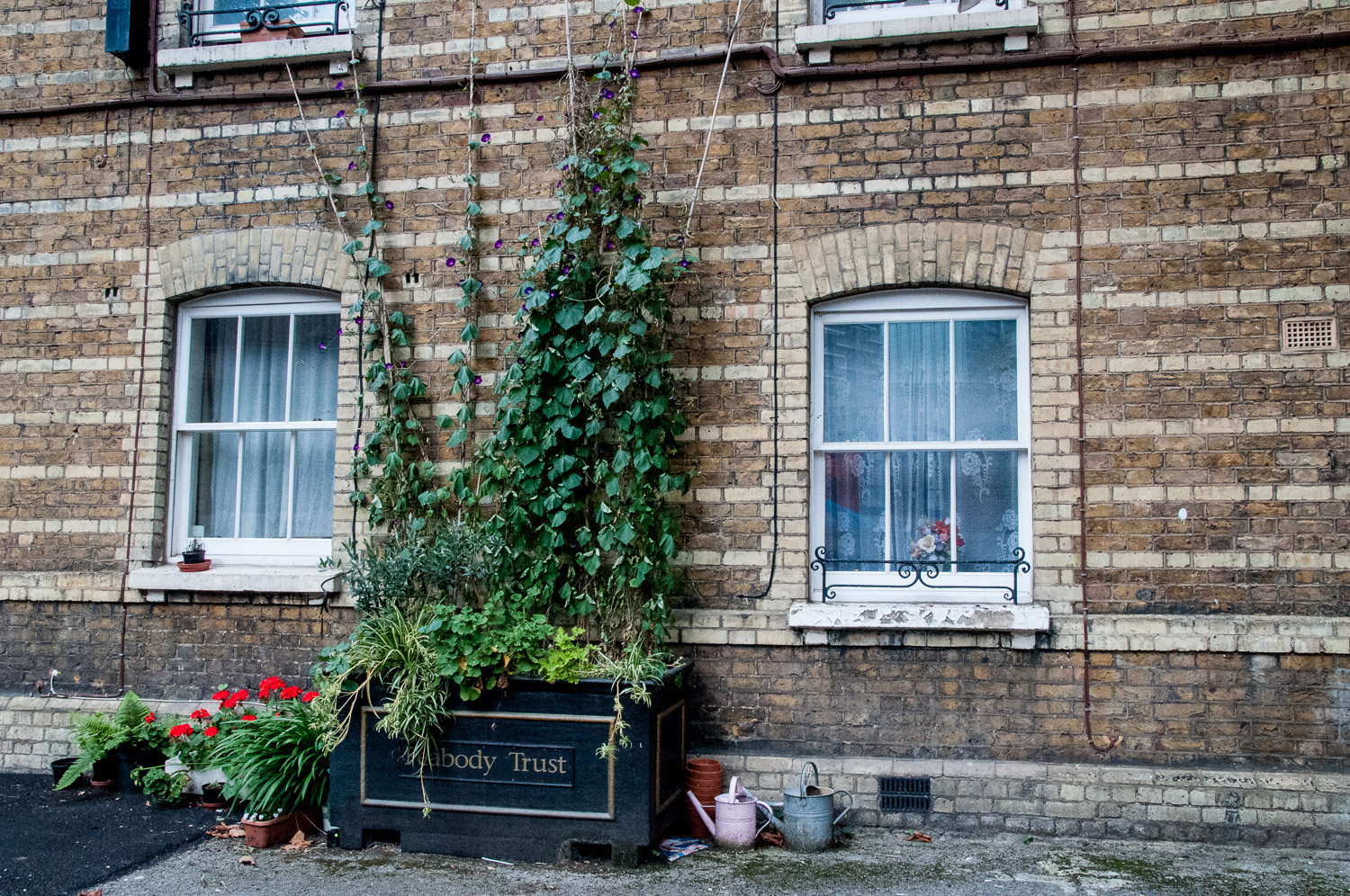
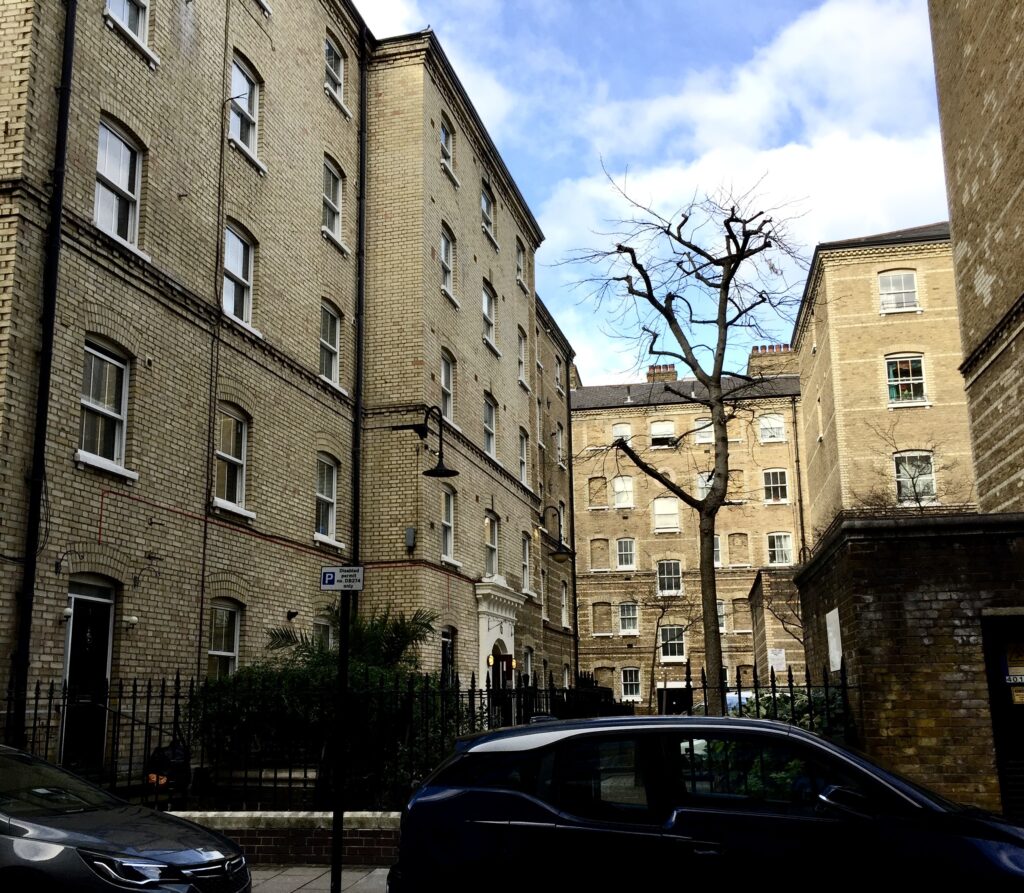
Nearby there’s a cabinet dedicated to the great philanthropist George Peabody (1795-1869). In retirement he devoted himself to charitable causes setting up a trust, the Peabody Donation Fund, to assist ‘the honest and industrious poor of London’. The Peabody Trustees would use the fund to provide ‘cheap, clean, well-drained and healthful dwellings for the poor’ with the first donation being made in 1862. The exhibition contains an illustration of the estate at Clapham Junction …
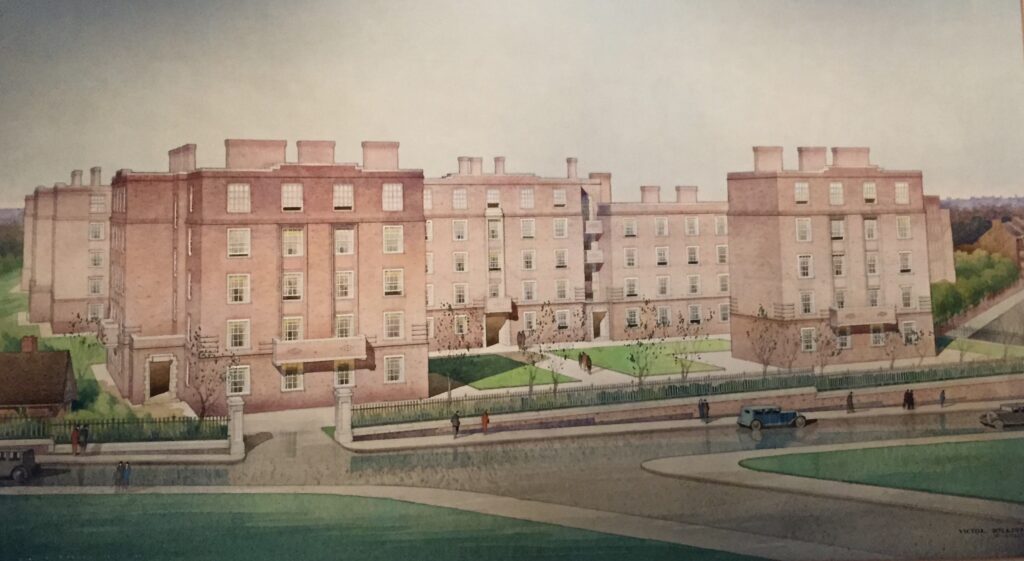

My ‘local’ estate is the one on Whitecross Street and dates from 1883 – the design is very typical Peabody, with honey coloured bricks and a pared down Italianate style …



Here he sits, looking pretty relaxed, at the northern end of the Royal Exchange Buildings …
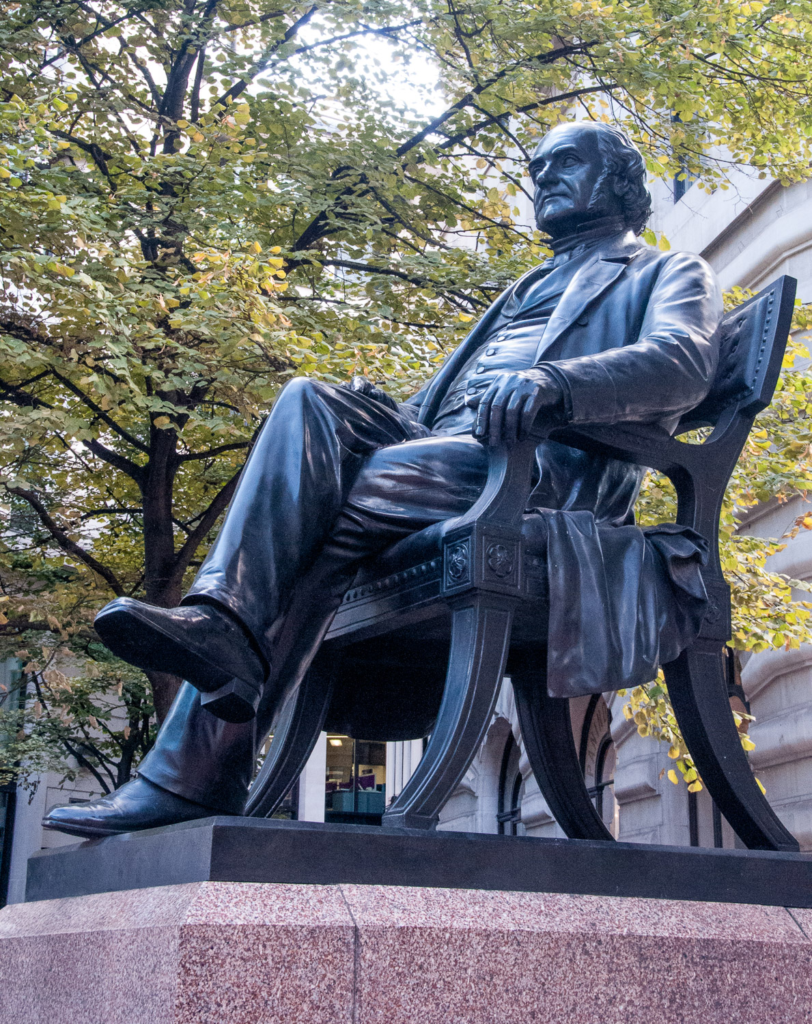

You can read more about him here in my blog City Living.
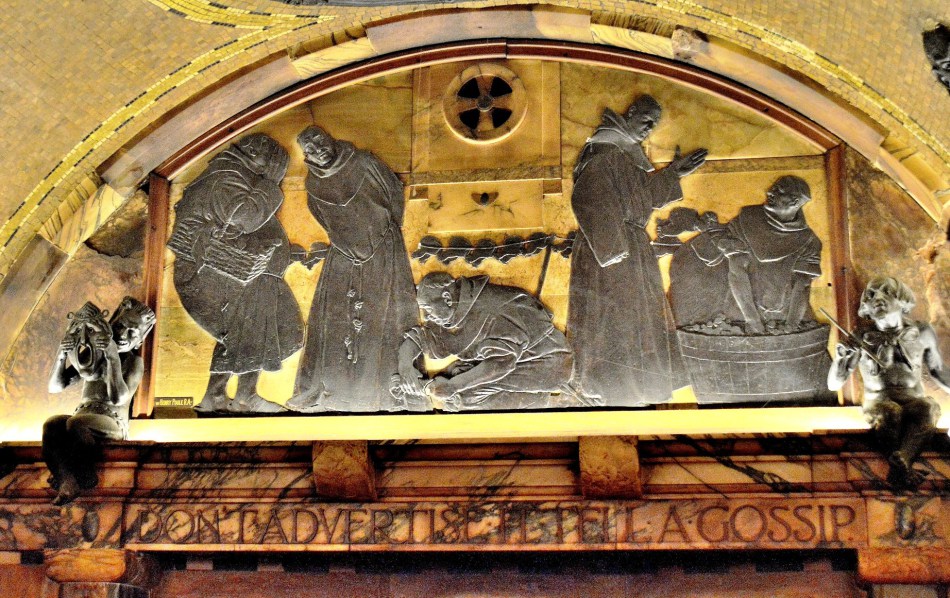
The Assize of Bread and Ale was a 13th-century law which regulated the price, weight and quality of the bread and beer. This medieval custumal (collection of customs) has drawings of bakers at work and others being punished for selling underweight loaves …

The punishment for the first offence was to be dragged through the city with the offending loaf around the person’s neck …
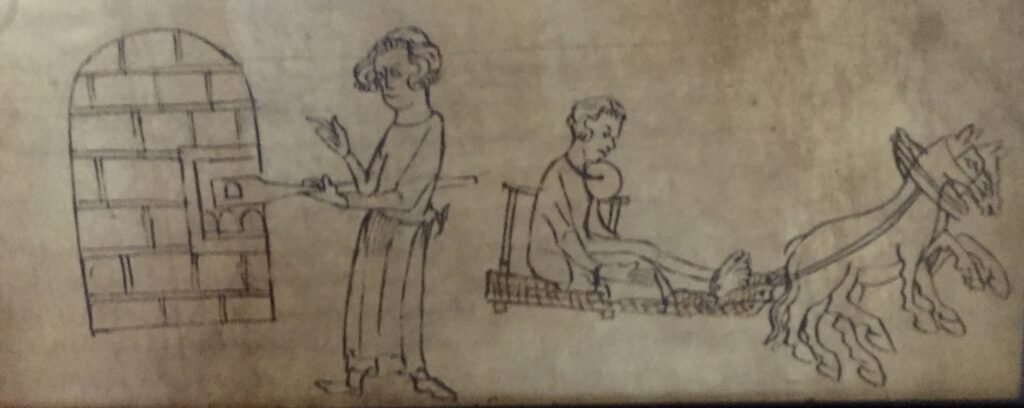

Incidentally, a second offence punishment was to be put in the pillory for an hour …
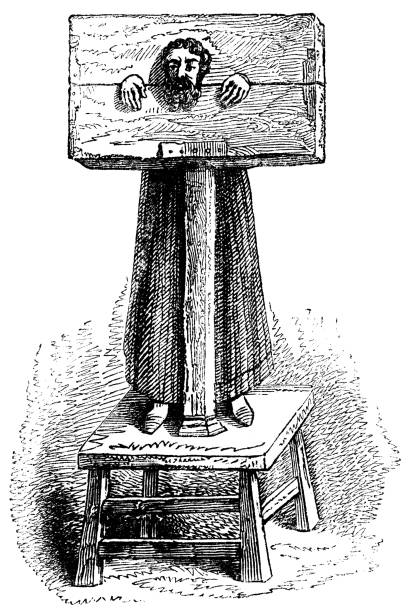
This may not sound like much but in addition to being jeered and mocked, those in the pillory might be pelted with rotten food, mud, offal, dead animals, and animal excrement. Sometimes people were killed or maimed in the pillory because crowds could get too violent and pelt the offender with stones, bricks and other dangerous objects.
On committing a third offence the baker’s oven was pulled down. This was the end of the person’s business, so unless someone bailed them out, they would be destitute.
The legislation was continually updated as this poster from 1905 illustrates …

At the Gallery there are films running showing, among other scenes, glimpses of the 1960 Lord Mayor’s show …



There are two paintings of a show near the main gallery entrance. This is 12:18 and 10 seconds (2010) by Carl Laubin …
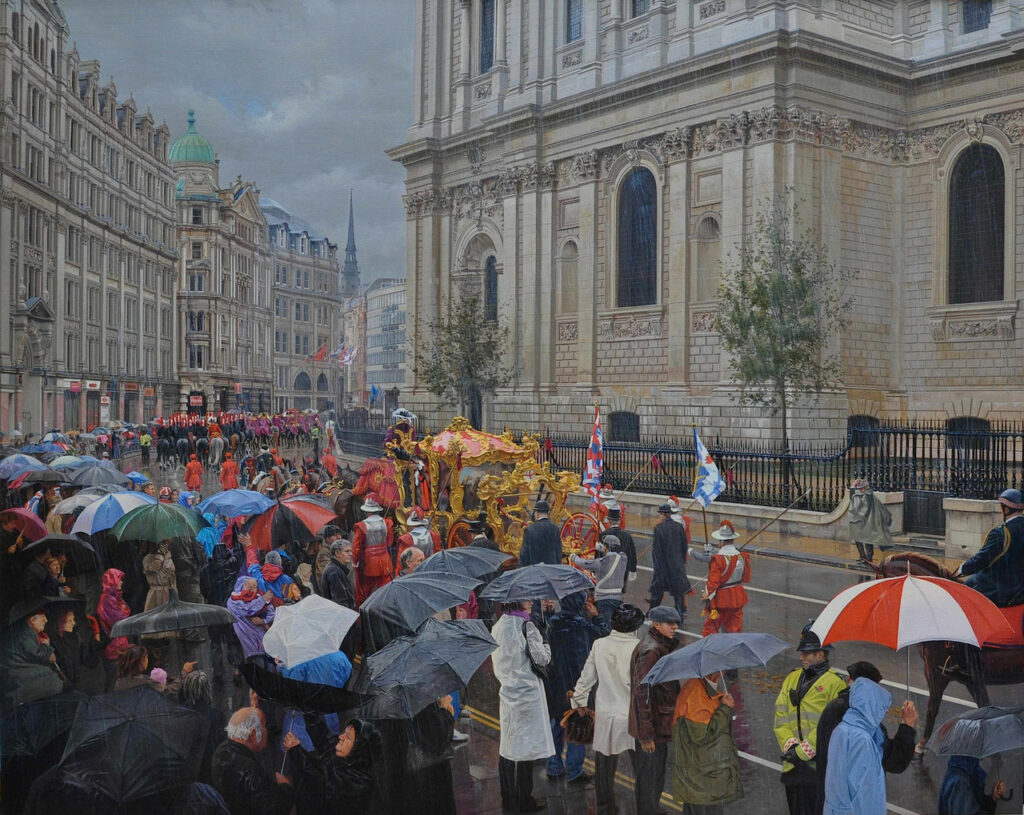

The other is one of my favourites, William Logsdail’s painting entitled The Ninth of November 1888 …
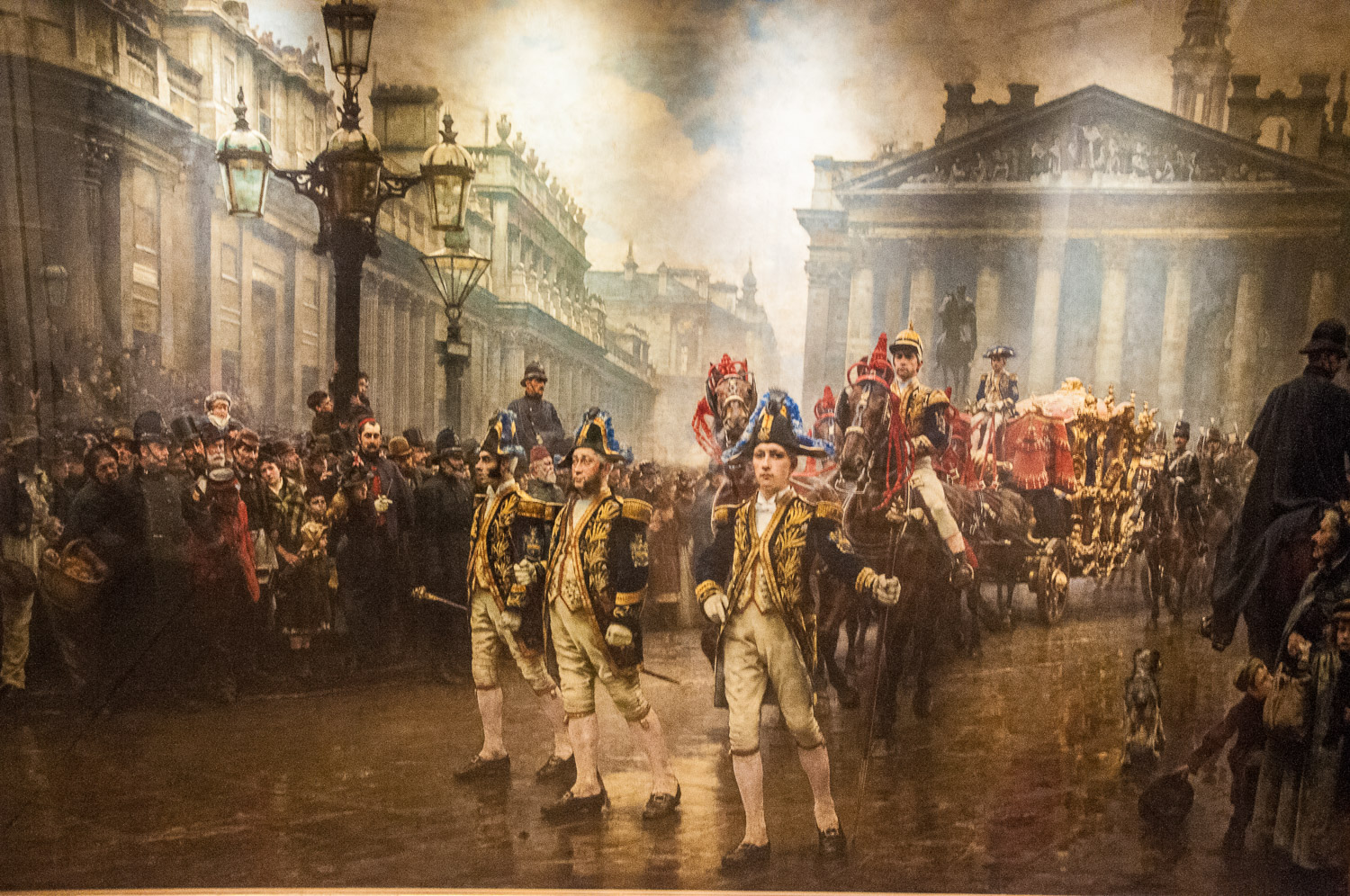
Although it’s the Lord Mayor’s procession in this picture he is nowhere to be seen and the artist has concentrated on the liveried beadles (who he actually painted in his studio)…
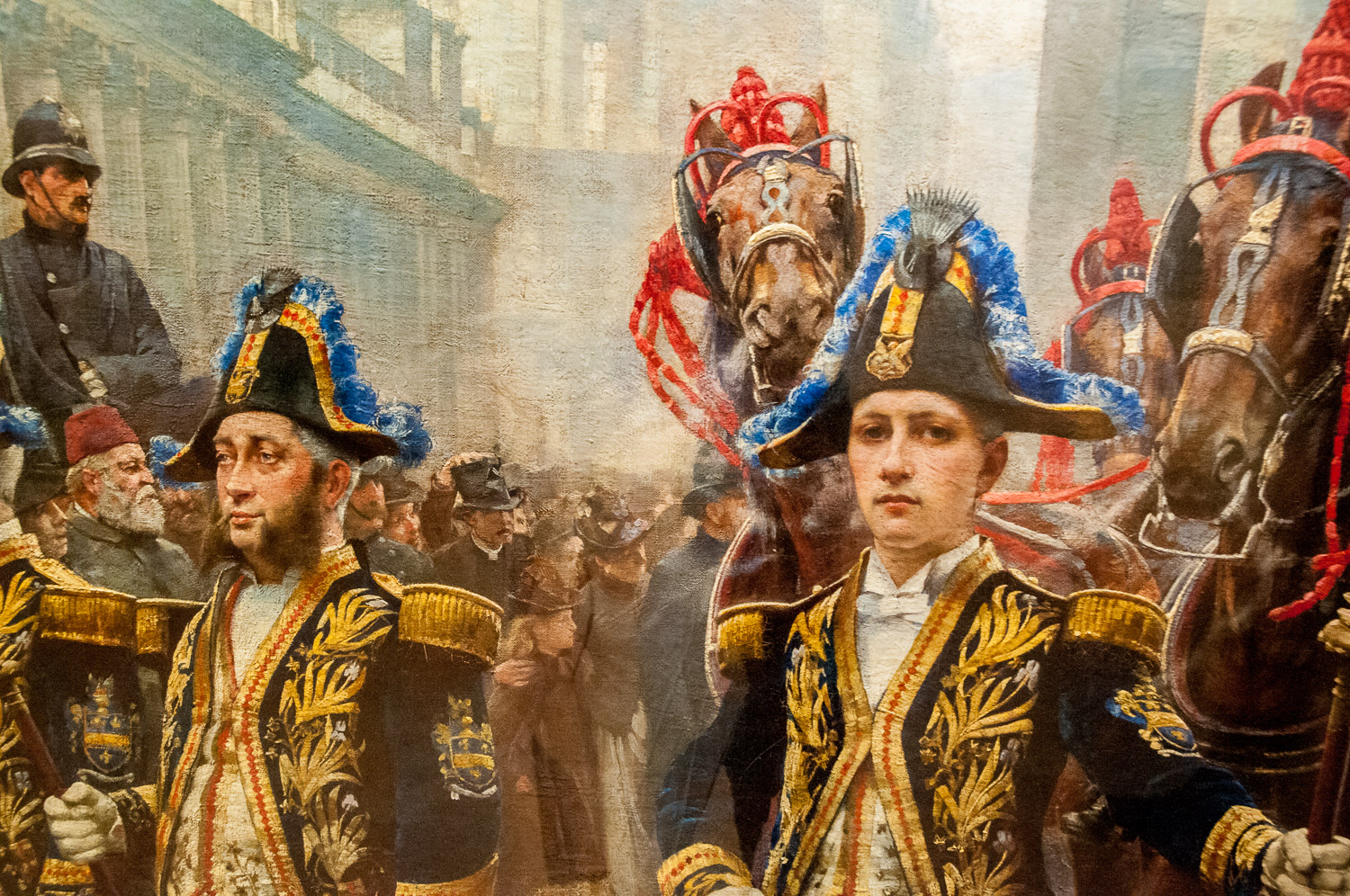

… and the people in the crowd …
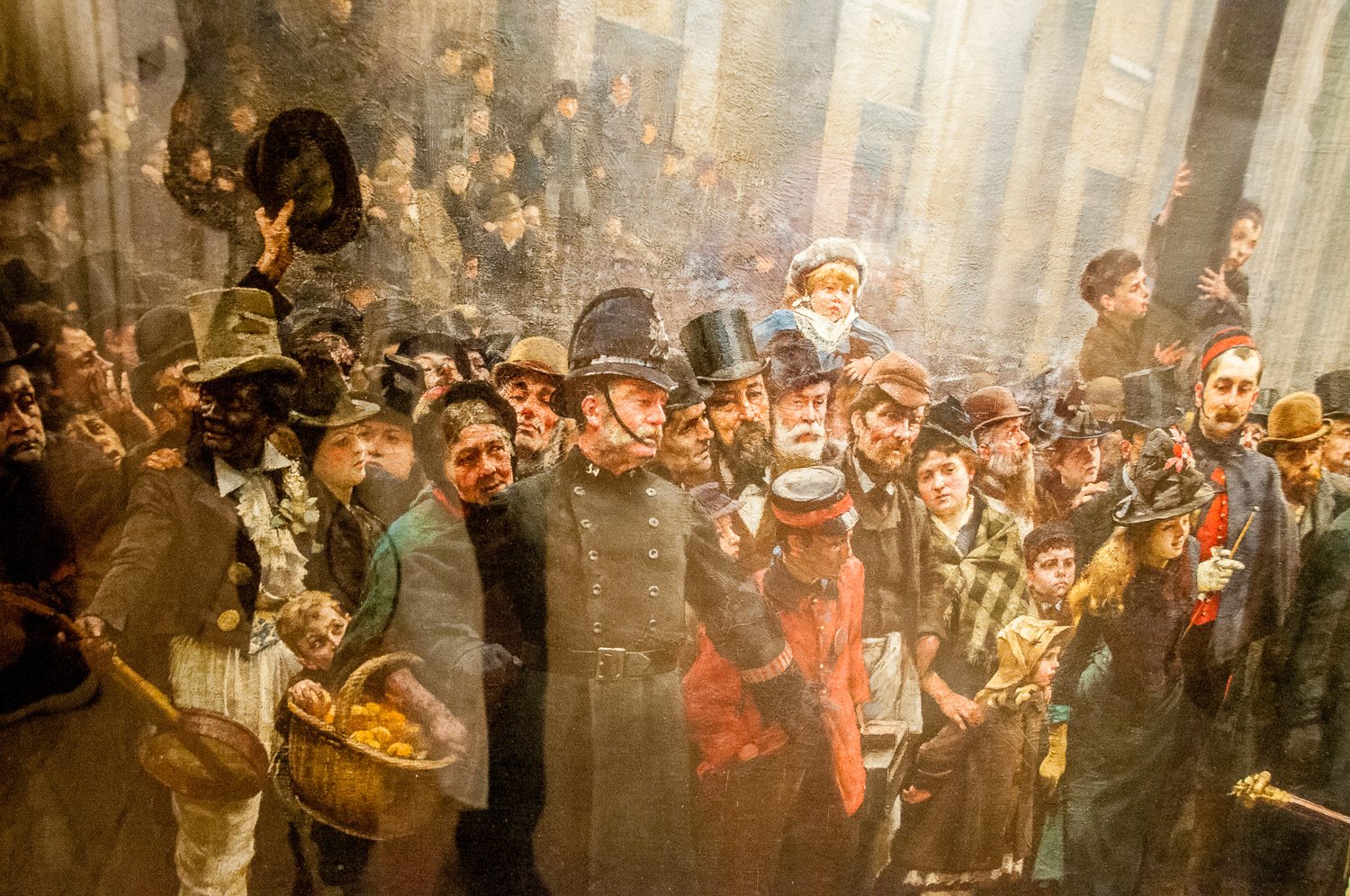
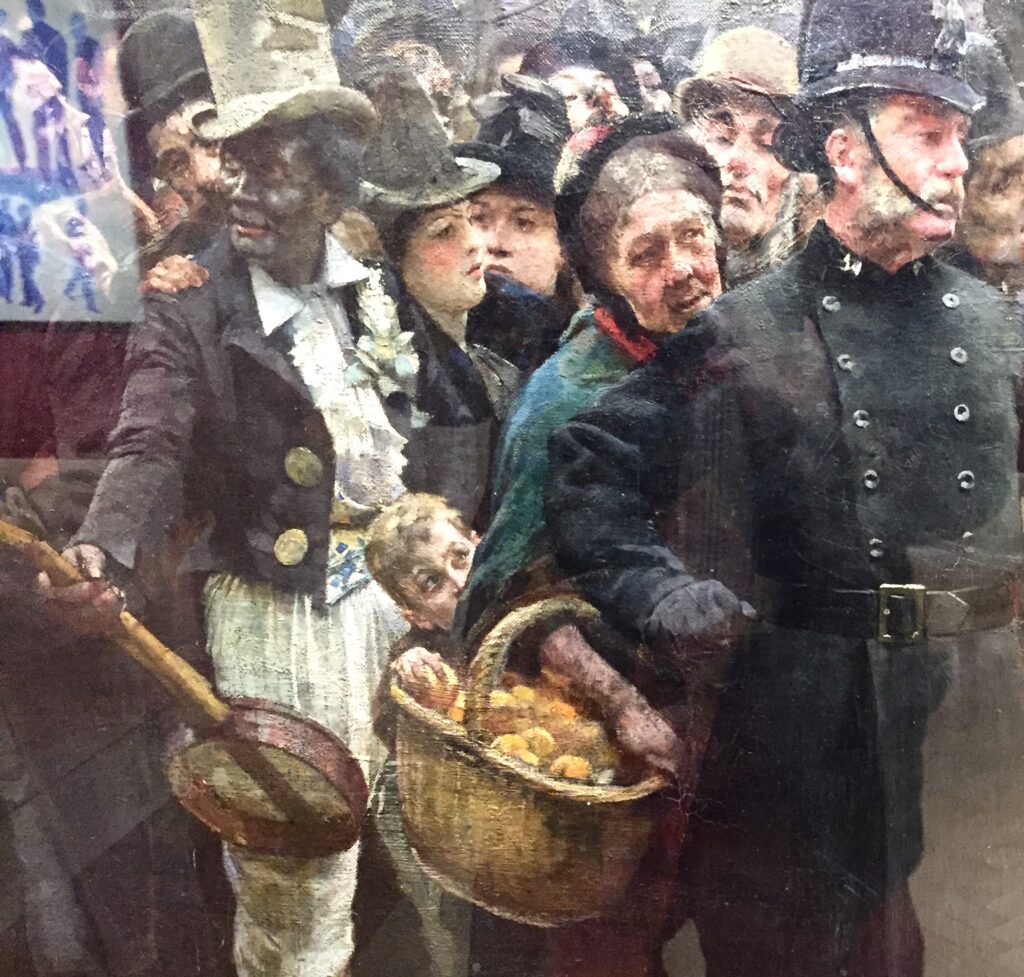
There is a minstrel in blackface with his banjo and next to him a little boy is nicking an orange from the old lady’s basket. On the right of the picture the man in the brown hat, next to the soldier with the very pale face, is Logsdail’s friend the painter Sir James Whitehead.
Naughty boy!

It’s a sobering thought that, not far away in the East End that afternoon, police were discovering the body of Mary Kelly, believed to be the last of Jack the Ripper’s victims.
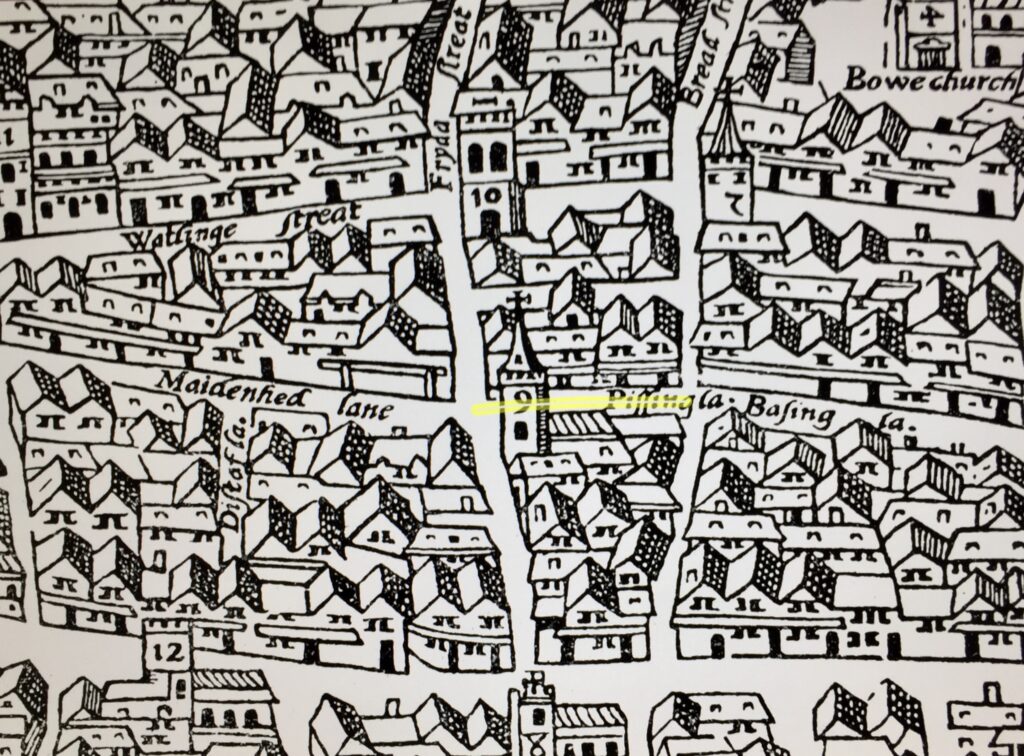
By the way, the Heritage room also has on permanent display a back lit illustration of the famous Agas Map …
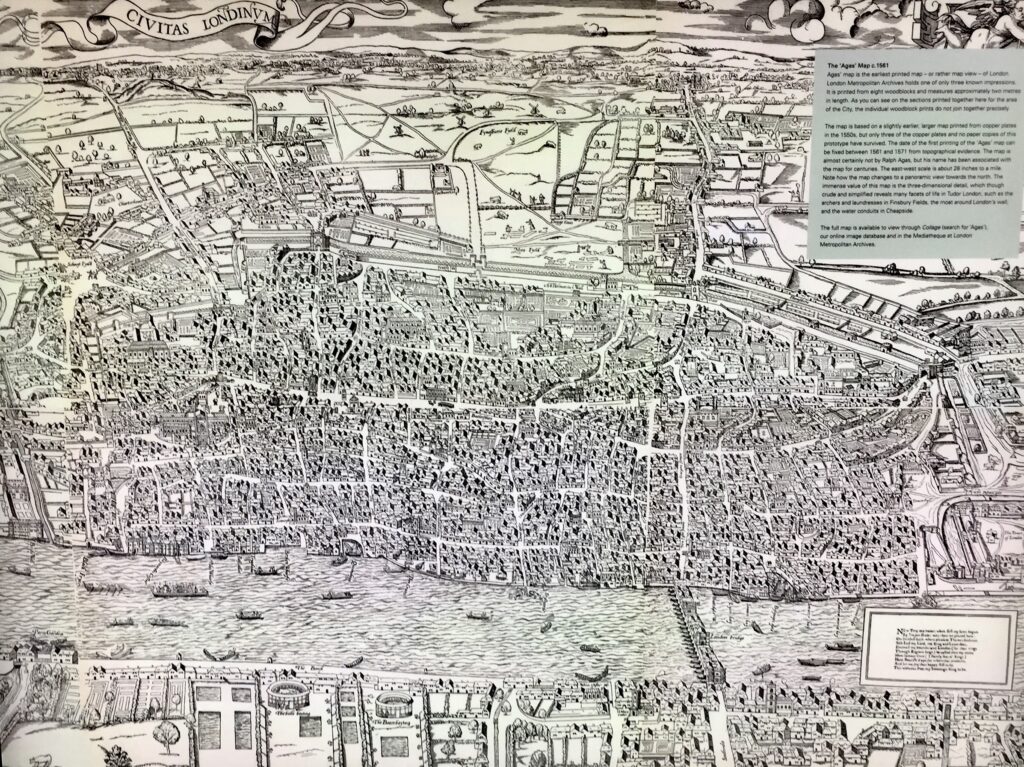
I have spent ages looking at it spotting street names that still exist today and open speces like Moorfields …
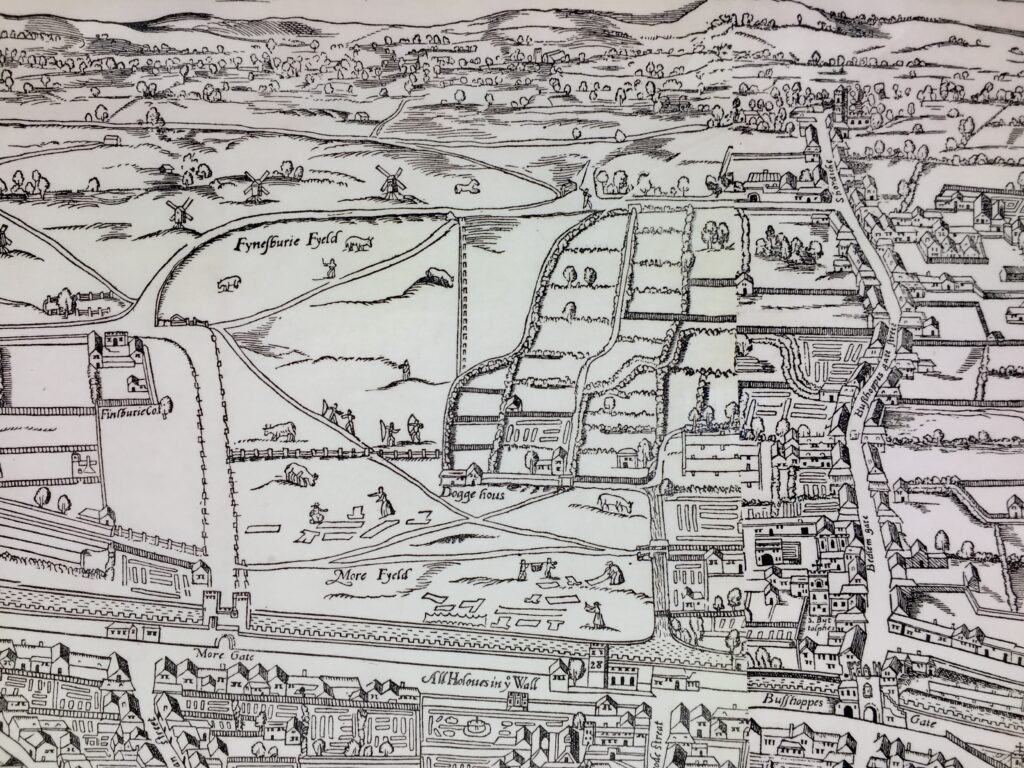
You’ll find an interactive version here, have fun exploring it.
If you would like to follow me on Instagram here is the link …