One day in the 1660s a young apprentice lad was due to meet his Master on London Bridge. Unfortunately, because he had no way of telling the time, he was late and severely castigated for his tardiness. Some fifty years later the young man, Charles Duncombe, had become immensely wealthy and, along with being knighted, had been elected Lord Mayor of London. The story goes that, the day he got into trouble, he promised himself that one day he would erect a public clock, so that all in the vicinity would know the time.
And we can still see today the clock he paid for and donated …
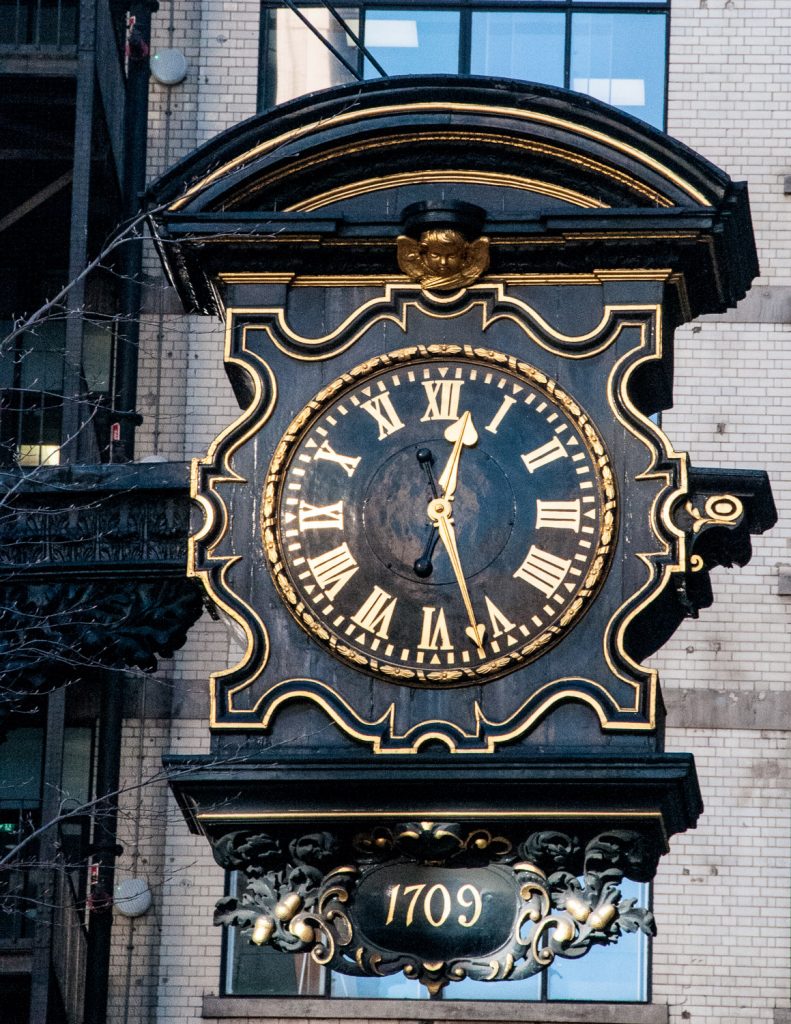

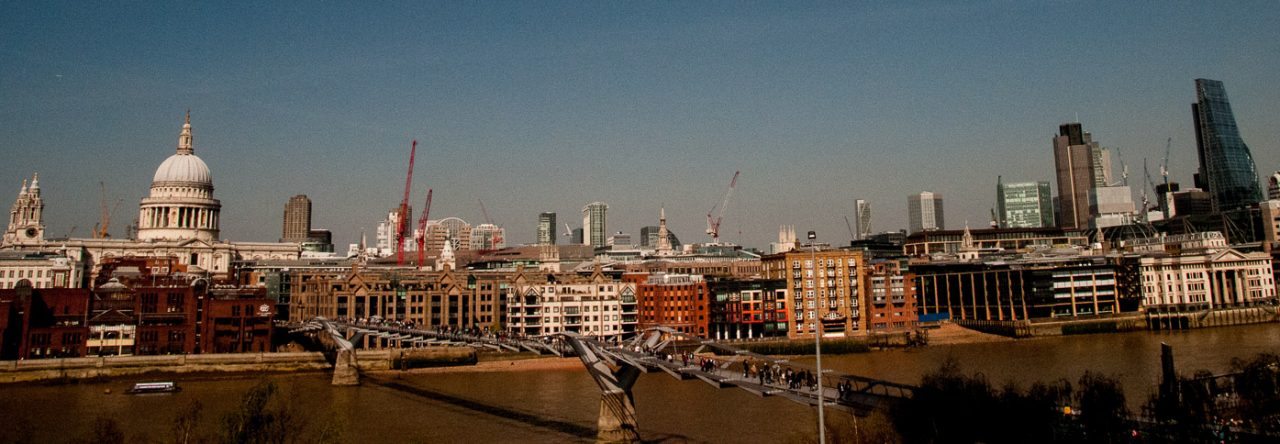
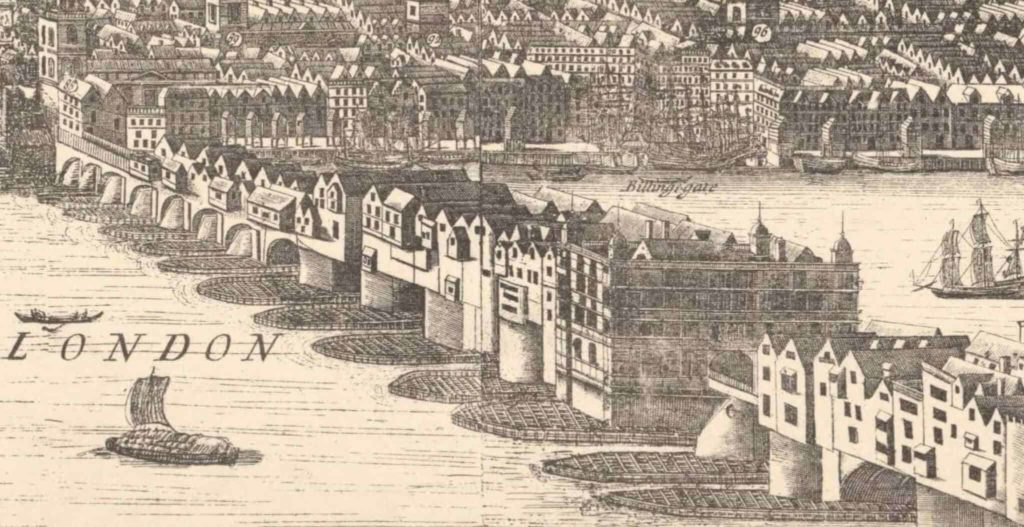
It’s at the side of the tower of St Magnus-the-Martyr, which once stood alongside the entrance to London Bridge until 1832, and so was highly visible both to people crossing the bridge and many in the City. Nowadays it is very hemmed in by office development …
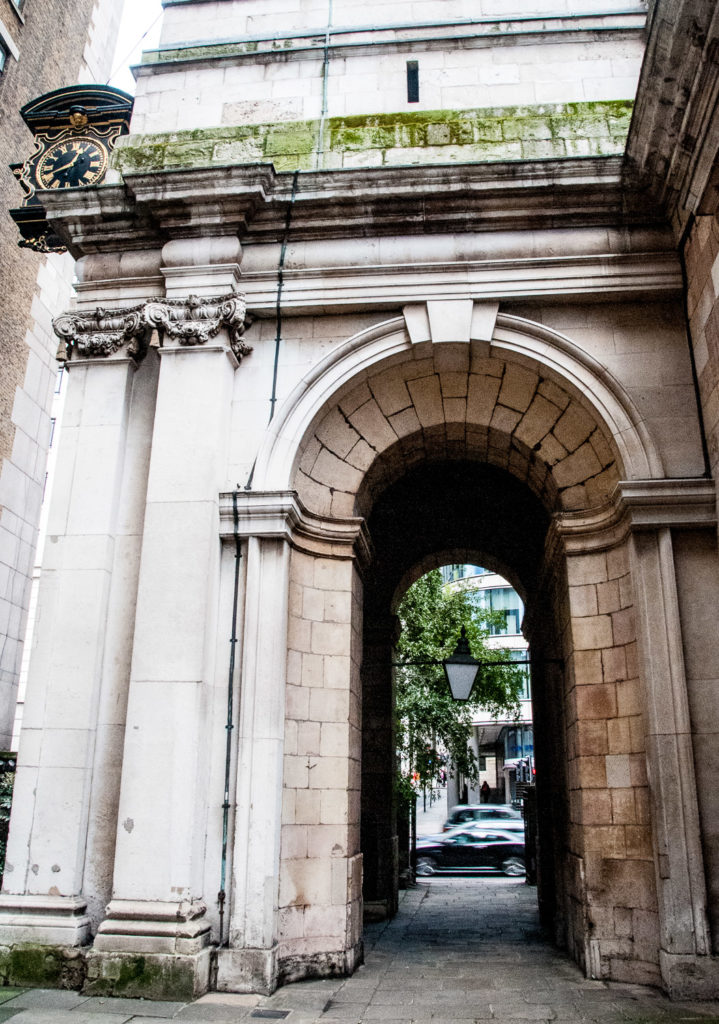

But its situation was quite different in the early 19th century …

You can see the clock and its proximity to the bridge in this etching by Edward William Cooke entitled Part of Old London-Bridge, St Magnus and the Monument, taken at Low-water, August 15th, 1831.
Now I have to say that, although Duncombe definitely donated the clock, there are some doubts about whether it was linked to a ‘promise’ he made as an apprentice. Nonetheless, it’s a nice story and so I thought it was appropriate to include it here.
I have always liked this clock at the corner of Fleet Street and Ludgate Circus …
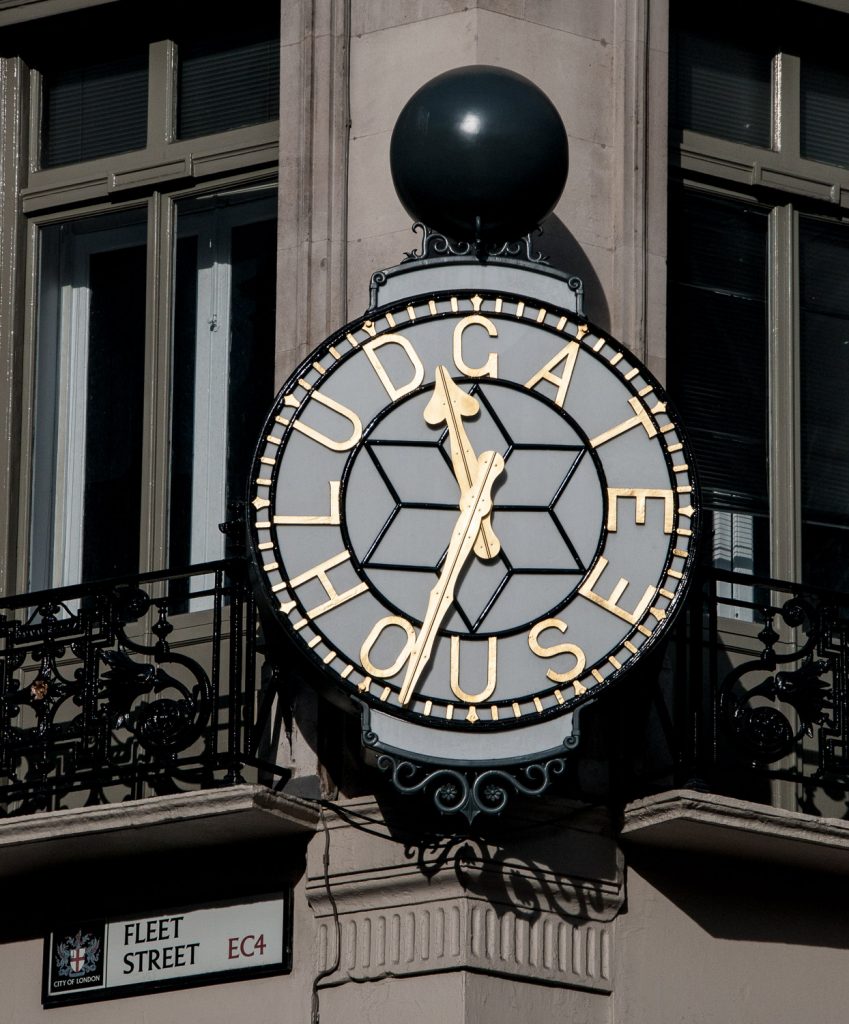

I read somewhere that, during the Blitz, an incendiary device became entangled in the ball at the top and dangled there for hours until it was deactivated. I often have this image in my head of gently swaying ordnance when I walk up Fleet Street.
And Fleet Street has a lot to offer when it comes to clock spotting.
How about this masterpiece …
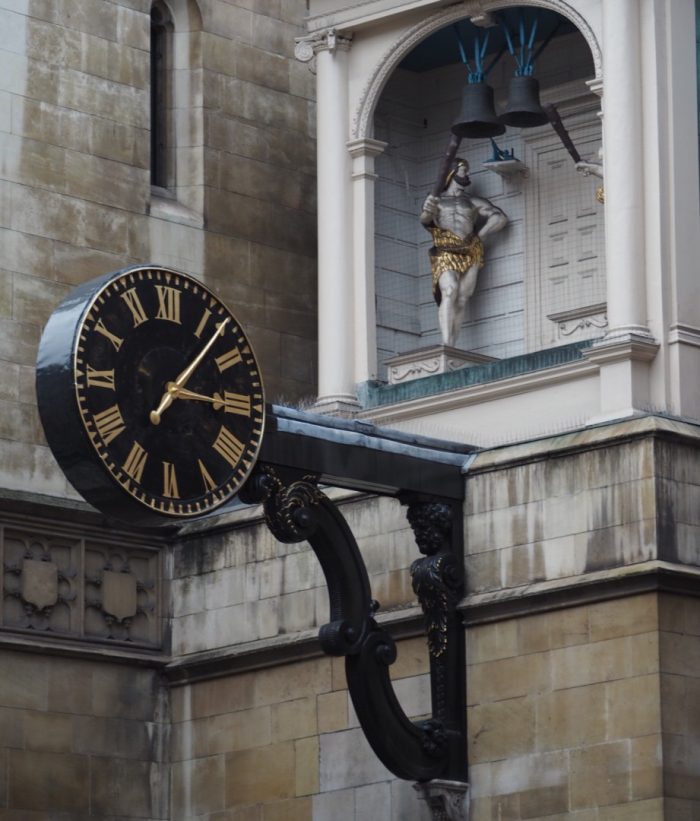

Installed just after the Great Fire of London in 1671, it was the first clock in London to have a minute hand, with two figures (perhaps representing Gog and Magog) striking the hours and quarters with clubs, turning their heads whilst doing so.
The present version of the clock was installed in 1738 before, in 1828, being moved to the 3rd Marquess of Hertford’s house in Regent’s Park. The Great War saw the Regent’s Park residence housing soldiers blinded from combat. The charity which undertook this went on to name itself after where the clock in the house came from: St Dunstan’s. It was returned to the Church in 1935 by Lord Rothermere to mark the Silver Jubilee of King George V.
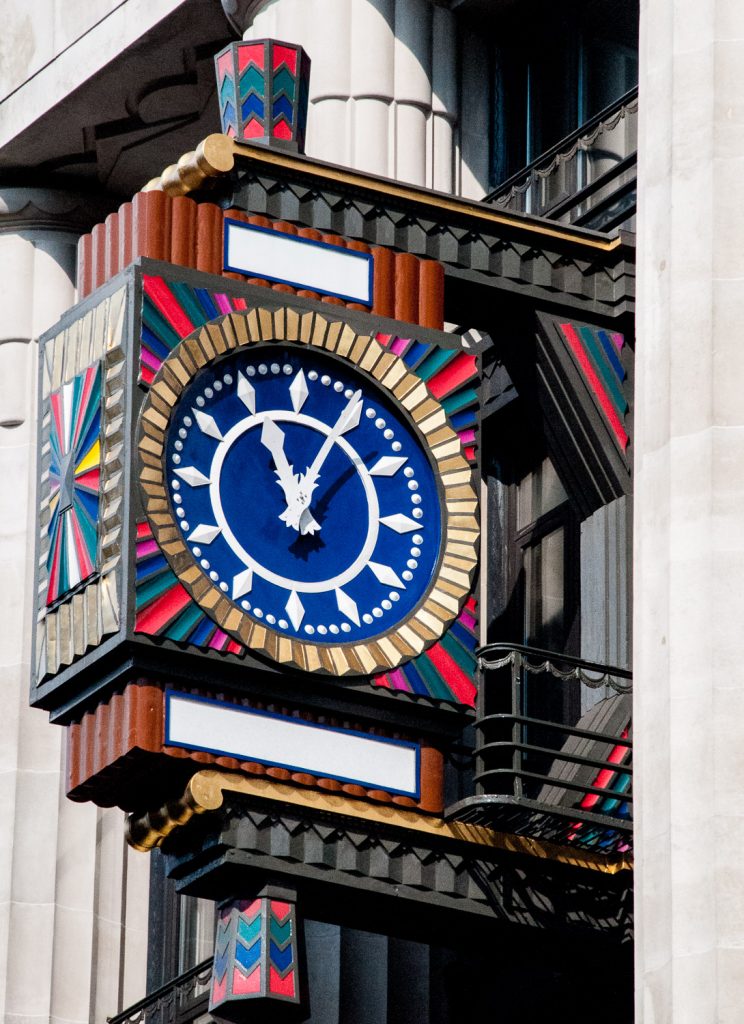
If you like the occasional burst of colour, look up at this Art Deco beauty outside the old Fleet Street offices of the Daily Telegraph (EC4A 2BB) …

Do any of you remember the original Number 1 Poultry, the 1870 Mappin & Webb building which, despite being listed, was demolished in 1994? Here is a picture taken a few years before demolition …
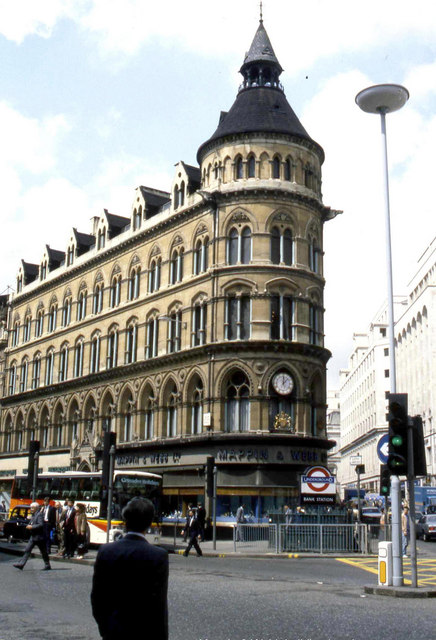

I was very familiar with the clock that faced the junction since, when I started work nearby and got off the Tube, it would indicate whether I was going to be late or not.
This is the new building that replaced it. I don’t dislike it, I’m just sad they felt they had to destroy the old one …

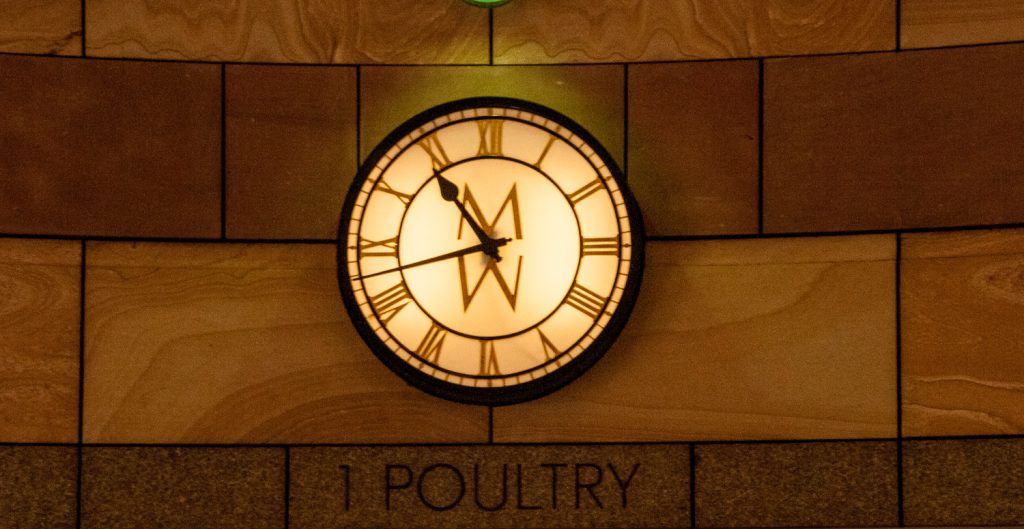
A small plus, I suppose, is that the old Mappin & Webb clock has been preserved in the public atrium …

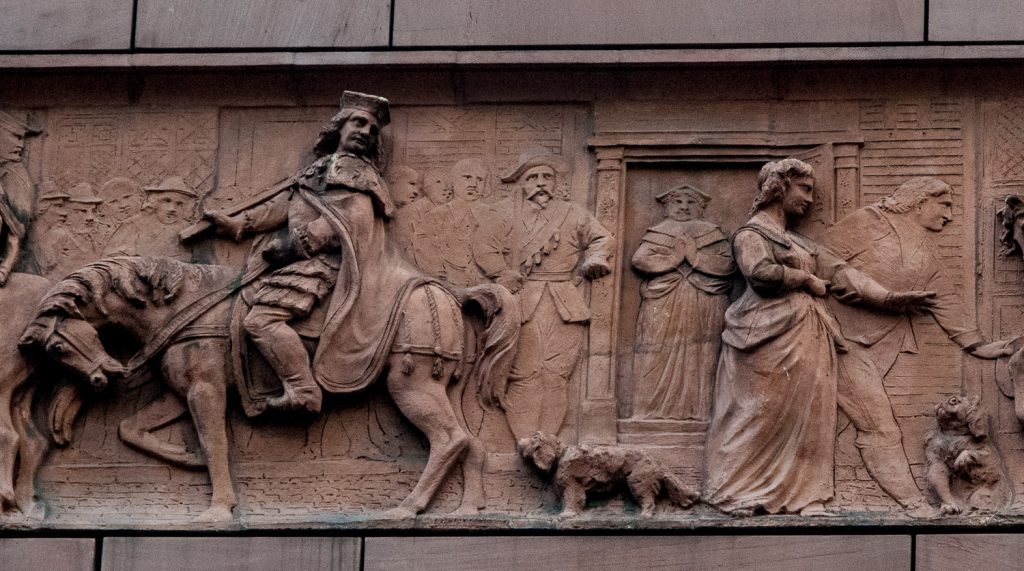
And a wonderful frieze from the old building illustrating royal processions has also been preserved and relocated facing Poultry. Here is a small section …

I am really pleased to report that the refurbishment of Bracken House is now complete and we can see again the extraordinary Zodiacal clock on the side of the building that faces Cannon Street (EC3M 9JA).
Here it is in all its glory …

If you look more closely at the centre this is what you will see …

On the gilt bronze sunburst at the centre you can clearly see the features of Winston Churchill. The building used to be the headquarters of the Financial Times and is named after Brendan Bracken, its chief editor after the war.
During the War Bracken served in Churchill’s wartime cabinet as Minister of Information. George Orwell worked under Bracken on the BBC’s Indian Service and deeply resented wartime censorship and the need to manipulate information. If you like slightly wacky theories, there is one that the sinister ‘Leader’ in Orwell’s novel 1984, Big Brother, was inspired by Bracken, who was customarily referred to as ‘BB’ by his Ministry employees.
The oddly-shaped Blackfriar pub on Queen Victoria Street sports a pretty clock just above the jolly friar’s head …
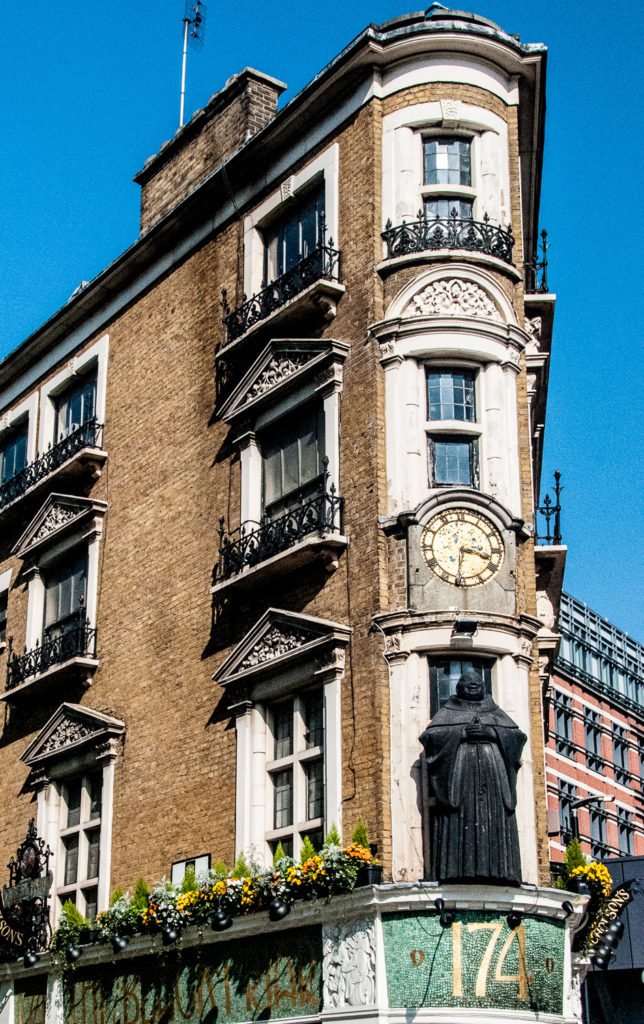

Unfortunately it hasn’t worked for long time.
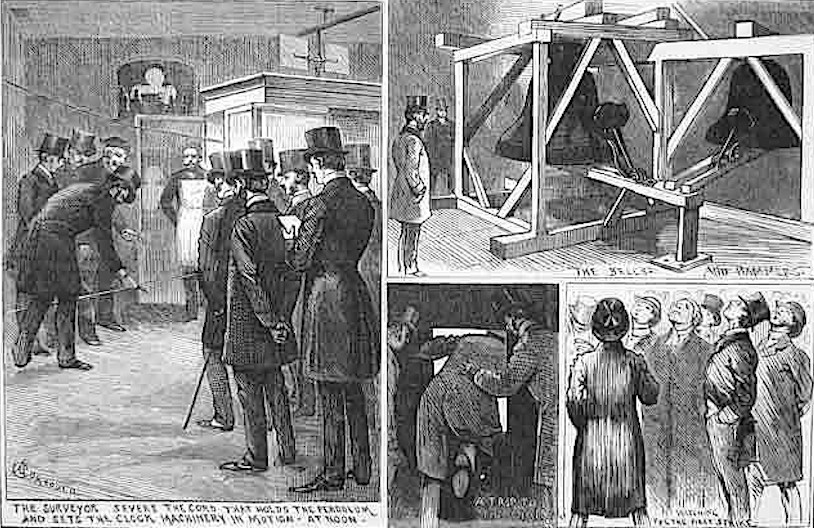
The Royal Courts of Justice have a magnificent clock (WC2A 2LL). It was ‘set in motion’ when ‘the surveyor severed the cord holding the pendulum’. Here’s the event as recorded in the Illustrated London News of December 1883 …

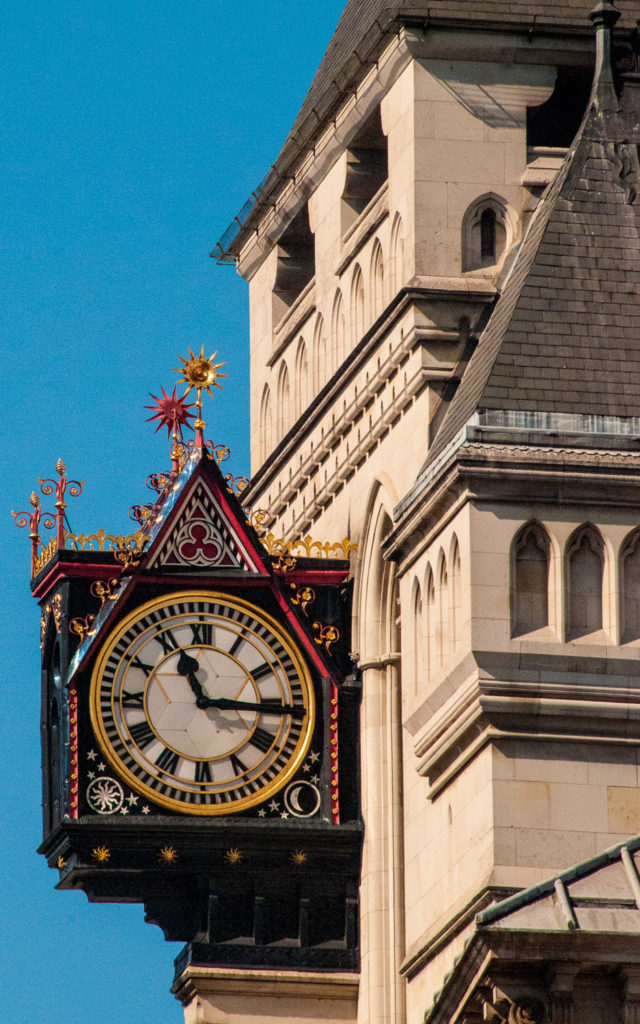
Designed by George Edmund Street, it has been described as ‘exuberant’ …

When doing research for this blog I discovered a tragic event relating to the clock. On 5th November 1954 a clock mechanic, Thomas Manners, was killed when his clothes were caught up in the machinery as he wound up the mechanism. He had been carrying out this task every week since 1937, as well as looking after the 800 or so other clocks in the law court buildings. You can read the press cutting I came across here.
The Royal Exchange has two ‘twin’ clocks, both exactly the same, one facing Threadneedle Street and one facing Cornhill …
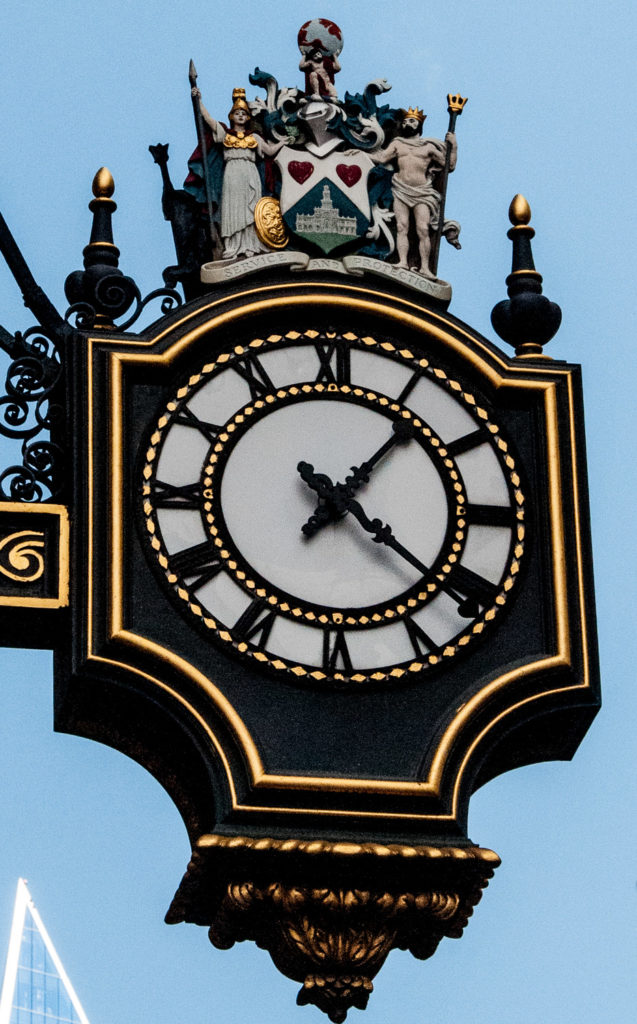

Britannia and Neptune hold a shield that contains an image of Gresham’s original Royal Exchange whilst above Atlas lifts a globe. I have seen it described as a Valentine’s Day clock because of the two red hearts. Ahhhh, sweet!
Clocks have featured regularly in my blogs and you can read more about some of them here and here.